Internal combustion engines (ICEs), hybrid vehicles, and electric vehicles continue to drive the development of new power semiconductor support technologies. Power devices in low-voltage and high-voltage applications need to operate at increasing frequencies, with greater immunity to interference and higher efficiency. The use of extended MOSFETs and IGBT devices in load management, power inverters, diesel/gasoline injectors, engine valves and motor drives has led to an increasing demand for automotive gate drivers.
The electrical structure of HEV/EV vehicles is gradually coordinated among all original equipment manufacturers. Common building blocks in turn drive semiconductor manufacturers to develop next-generation components that meet automotive standards (AECQ100 and Q101). Robust high current, high voltage MOSFETs, IGBTs, high voltage rectifiers and support control ICs are no longer rare. Fairchild's AECQ100 gate driver family includes all high current low side, high voltage IC (HVIC), high side and HVIC half bridge (high and low) side gate drivers for a wide range of applications.
The newest member of Fairchild's automotive gate driver portfolio extends the HVIC product line to the high peak current range required for inverter and motor drive applications. The FAN7171_F085 high-side and FAN7190_F085 high-side and low-side gate driver ICs are commonly used in monolithic automotive systems that operate at voltages up to +600V and require a variety of gate drivers.
High current low side gate driver
From piezoelectric injectors to low-power converter ground-source circuits, low-side gate drivers are commonly used to drive MOSFET single-gate drivers and dual-gate drivers with industry-standard pins that select input logic levels ( CMOS or TTL), enable or disable the circuit, and dual logic inputs. The output stage of Fairchild's low-end gate driver utilizes the Miller DriveTM architecture, which includes a bipolar device in parallel with the MOSFET. (Figure 1) This bipolar device is designed to provide high peak current for accelerating the transition through the Miller effect platform region during an on or off cycle. Parallel MOSFETs provide the lowest voltage drop.
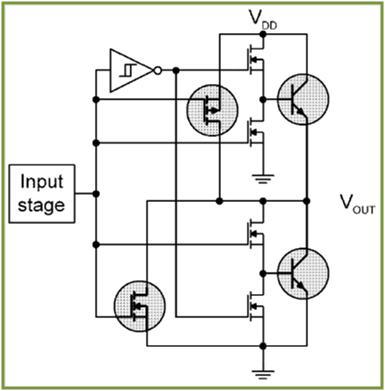
Figure 1. MillerDriveTM architecture output stage for high current low side gate drivers
Common uses include front-end MOSFETs in boost converters, MOSFETs and IGBTs for PFC front-ends that charge devices and MOSFETs in a ground-source configuration.
Dual 2A and dual 4A low-side devices are commonly used in the first phase of 50W to 500W AC power converters, using standard topologies ranging from 50kHz to 50kHz. The most common topology that can operate directly on a 12V battery supply is the push-pull configuration. The output voltage is typically between 170Vdc and 280Vdc. Another application for boost converters rated at 200W or higher is for HEV/EV high-voltage rail emergency Power Supplies, which can effectively “start†a faulty vehicle with only a 12V power supply.
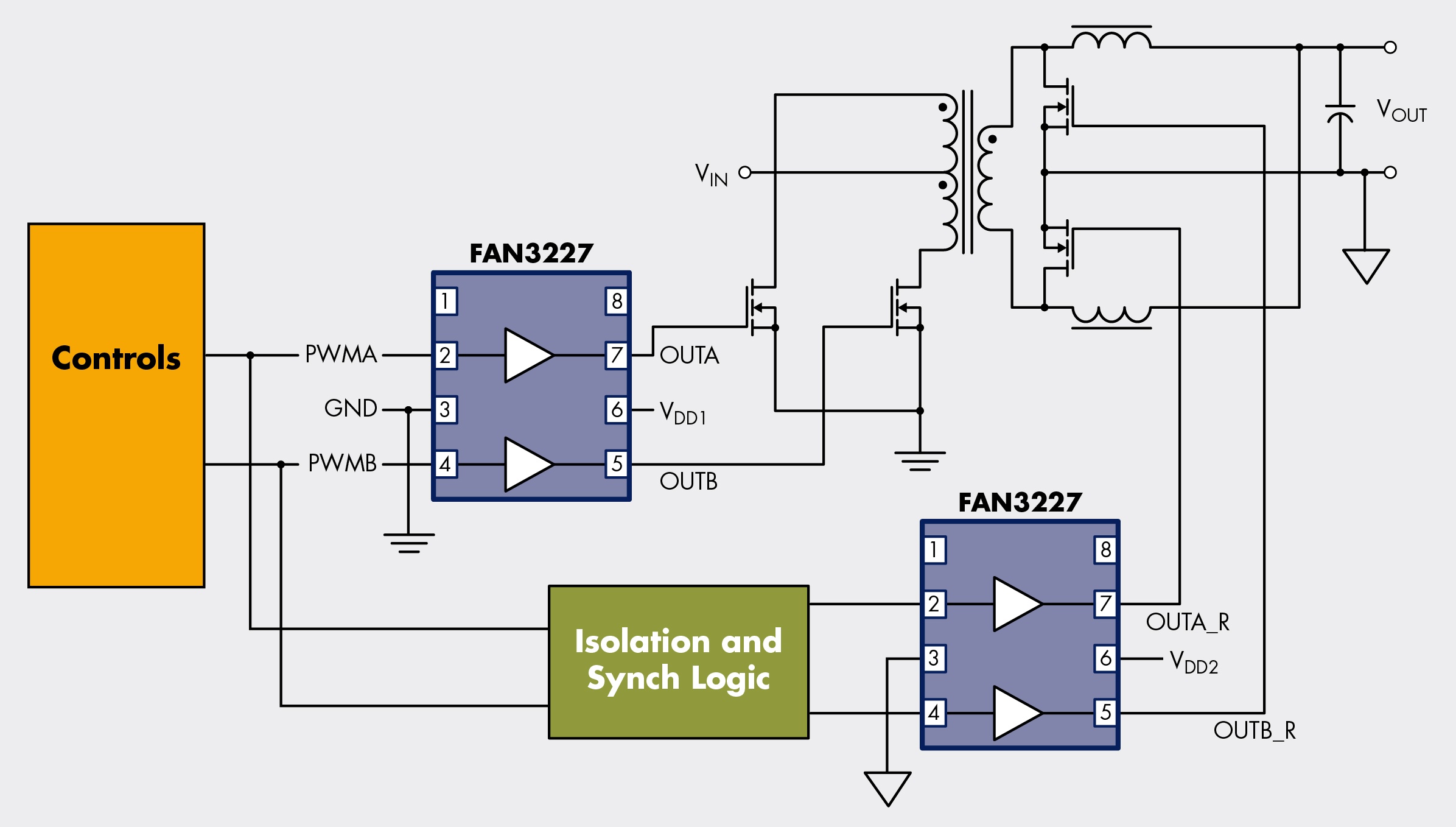
Figure 2 push-pull front end and synchronous rectifier output
Low power converters typically use a simple rectifier for output. However, high-voltage rectifiers can be replaced with synchronous rectification for higher output power and higher efficiency. As shown in Figure 2, a dual-channel low-side, high-current gate driver such as the FAN3227_F085 is used to drive the MOSFET.
Power Inverter,Pure Sine Wave Inverter For Outdoor,300W Power Inverter,Mini Power Inverter
GuangZhou HanFong New Energy Technology Co. , Ltd. , https://www.hfsolarenergy.com