Gas sensors are primarily used to detect a specific gas, measure whether it is present near the sensor, or the amount of air in the vicinity of the sensor. Therefore, gas sensors are often indispensable in safety systems. These sensors provide information on the flammable, flammable and toxic gases in the safety system, as well as the oxygen consumption in the area, the proportion of carbon dioxide.
Common gas sensors include electrochemical gas sensors, catalytic combustion gas sensors, semiconductor gas sensors, infrared gas sensors, and the like. Different types of sensors have different principles and structures, and their performance, usage, applicable gas, and applicable occasions are also different. Today, we will list the common types of gas sensors for everyone, and hope to help everyone.
Electrochemical gas sensorA considerable portion of flammable, toxic and harmful gases, such as hydrogen sulfide, nitrogen monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, sulfur dioxide, carbon monoxide, etc., are electrochemically active and can be electrochemically oxidized or reduced. By using these reactions, gas components and gas concentrations can be distinguished. Electrochemical sensors are based on this principle.
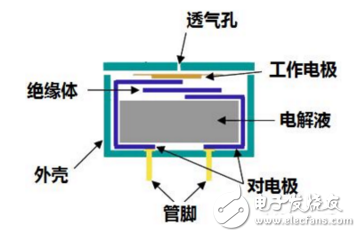
Primary battery type gas sensor
Such a sensor is also called a Gaffani battery type gas sensor, or a fuel cell type gas sensor or a spontaneous battery type gas sensor. Their principle is the same as the dry battery we use every day, except that the battery carbon-manganese electrode is replaced by a gas electrode. Taking an oxygen sensor as an example, the oxygen cathode is reduced and the electronic ammeter flows to the anode where the lead metal is oxidized. Therefore, the magnitude of the current is directly related to the oxygen concentration. This sensor can effectively detect oxygen, sulfur dioxide, chlorine and other gases.
Constant potential electrolytic cell type gas sensor
This sensor is very effective for detecting reducing gases. Its principle is different from that of galvanic sensors. The electrochemical reaction is forced by current and is a true Coulomb analysis sensor. This kind of sensor has been successfully used in the detection of carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, hydrogen, ammonia, helium and other gases. It is currently the mainstream sensor for the detection of toxic and harmful gases.
Note: Coulomb analysis refers to the method of determining the content of the substance to be tested by Faraday's law according to the amount of electricity consumed during the electrolysis process.
Concentration battery type gas sensor
The sensor has electrochemically active gas on both sides of the electrochemical cell, and spontaneously forms a concentrated electromotive force. The magnitude of the electromotive force is related to the concentration of the gas. A successful example of such a sensor is an oxygen sensor for a vehicle and a solid electrolyte type carbon dioxide detection. instrument.
Limit current type gas sensor
This is a sensor for measuring the oxygen concentration. The working principle is based on the action of an oxygen pump that stabilizes the zinc oxide solid electrolyte, and the limiting current is obtained by controlling the oxygen supplied to the cathode by gas diffusion. This type of sensor is currently used primarily for combustion control of boilers, oxygen concentration detection in molten steel, and oxygen detection in automobiles.
Semiconductor gas sensor
Semiconductor gas sensors use the oxidation and reduction of gases on the surface of the semiconductor to cause changes in the resistance of sensitive components:
A gas having a tendency to adsorb negative ions such as oxygen is used as an oxidizing gas-electron-receiving gas;
A gas having a tendency to adsorb positive ions such as hydrogen, a carbon oxide compound or an alcohol is called a reducing gas-electron supply type gas.
When an oxidized (reduced) type gas is adsorbed onto an N(P) type semiconductor, carriers of the semiconductor are reduced (increased), and resistivity is increased (decreased); when adsorbed onto a P(N) type semiconductor, carriers of the semiconductor are increased. (decreased), the resistivity drops (rises). (It can be seen that the oxidized and reduced semiconductors are diametrically opposed) and thus the corresponding gases can be effectively detected from these properties.
Semiconductor gas sensors can be effectively used for many gas detections such as methane, ethane, propane, butane, alcohol, formaldehyde, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, ethylene, acetylene, vinyl chloride, styrene, and acrylic acid. In particular, such sensors are inexpensive and can meet both industrial and residential needs.
Disadvantages: Poor stability, greatly affected by the environment, should not be used in places where measurement accuracy is required.
Catalytic combustion gas sensor
The sensor is actually a gas sensor based on a platinum resistance temperature sensor, that is, a high temperature resistant catalyst layer is prepared on the surface of the platinum resistor. At a certain temperature, the combustible gas is catalytically burned on the surface, so the platinum resistance temperature rises, resulting in resistance. Resistance changes.
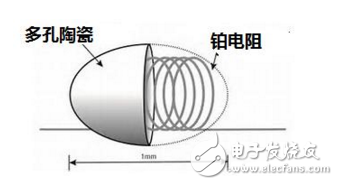
Since the catalytic combustion gas sensor is usually surrounded by a porous ceramic ceramic bead, the sensor is usually also used as a catalytic bead gas sensor. In theory, this sensor can detect all gases that can be burned, but there are many exceptions in practical applications. Such sensors are commonly used to detect combustible gases such as methane, LPG, and acetone in the air.
Based on the excellent temperature characteristics of platinum resistors, this sensor has accurate measurement and fast response. The sensor output is directly related to the environmental explosion hazard. The safety detection field is a class of dominant sensors.
The disadvantage is that it needs to work in a sufficient oxygen environment (after all, it needs to be burned); the dark fire works, there is a danger of ignition and explosion; most of the organic vapors of the elements have poisoning effect on the sensor; due to the continuous consumption of the catalyst, the zero point and the range will drift. Frequent calibration and adjustment are required.
Pre-Terminated Mini Cable,Pre Terminated Double Sheath Cable,Pre-Terminated Cable For 5G Network,Pre Terminated Cable For Telecommunication
ShenZhen JunJin Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.jjtcl.com