In electric vehicles, electric motors are a very important key component. Have we introduced the types of electric motors? What are the performance characteristics of the motor? This article analyzes how two different types of motors generate power!
How does the AC asynchronous motor generate power?
The working principle of the AC motor: the energized winding rotates in a rotating magnetic field.
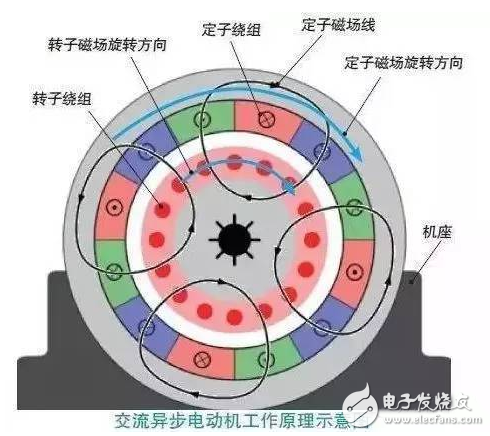
The stator and rotor in the motor are not in contact. Why does the rotor rotate after the AC winding is applied to the stator winding? Its working principle is applied to two major electromagnetic laws: Faraday's law and Lenz's law.
When the winding wound on the stator is connected to an alternating current, the stator winding generates a rotating electromagnetic field due to the characteristics of the alternating current. The winding on the rotor is a closed-loop conductor that is in the rotating magnetic field of the stator and is equivalent to continuously cutting the magnetic induction line of the stator. According to Faraday's law, when a part of the closed conductor is used to cut the magnetic induction line in the magnetic field, a current is generated in the conductor, and this current forms an electromagnetic field.
Thus, there are two electromagnetic fields in the motor: one is the stator electromagnetic field generated after the external alternating current is turned on; the other is the rotor electromagnetic field formed by the current generated by cutting the stator electromagnetic induction line. According to Lenz's law, the magnetic field of the induced current always opposes the cause of the induced current (the rotor winding cuts the magnetic induction line of the stator electromagnetic field), that is, the magnetic induction line that tries to make the conductor on the rotor no longer cut the stator magnetic field. The result is: The conductor on the rotor "catches up" the rotating electromagnetic field of the stator, that is, rotates the rotor with the rotating electromagnetic field of the stator, eventually causing the motor to start rotating.
Since the rotor is always "catch-up" to the rotational speed of the stator electromagnetic field, and in order to be able to cut the magnetic induction line to generate an induced current, the rotational speed of the rotor is always a little slower than the rotational speed of the stator electromagnetic field (about 2% to 5%), that is, Asynchronous operation, so the motor that generates the induced current is called an AC asynchronous motor.
The following is the construction of a one-way AC motor:
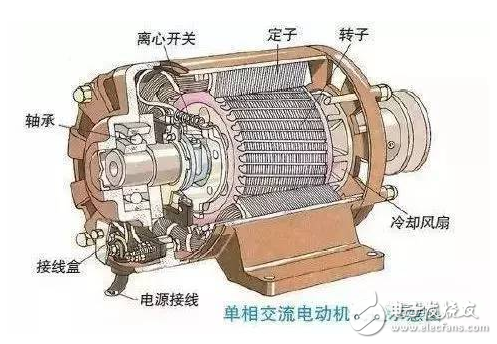
The GM AC asynchronous motor is constructed as follows:

How does a permanent magnet synchronous motor generate power?
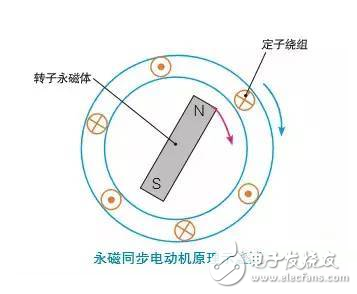
In an AC asynchronous motor, the rotor magnetic field is formed in two steps: the first step is that the stator rotating magnetic field first induces current in the rotor winding; the second step is to induce current to generate the rotor magnetic field. Under the action of Lenz's law, the rotor follows the rotating magnetic field of the stator, but it "can never catch up", so it is called an asynchronous motor. If the current in the rotor winding is not induced by the rotating magnetic field of the stator, but is generated by itself, the rotor magnetic field is independent of the rotating magnetic field of the stator, and the magnetic pole direction is fixed. Then, according to the principle of homosexual repulsive and opposite-phase attracting, the stator The rotating magnetic field pulls the rotor to rotate and rotates the rotor field and the rotor in synchronism with the stator's rotating magnetic field. This is how the synchronous motor works.
According to the different ways of generating the self-generated magnetic field of the rotor, the synchronous motor can be divided into two types:
First, the rotor winding is connected to an external direct current (excitation current), and then the excitation current generates a rotor magnetic field, thereby rotating the rotor and the stator magnetic field synchronously. Such a synchronous motor that generates a rotor magnetic field from an exciting current is called an exciting synchronous motor.
The second is to simply embed a permanent magnet on the rotor to directly generate a magnetic field, eliminating the need for excitation current or induced current. Such a synchronous motor that generates a rotor magnetic field from a permanent magnet is called a permanent magnet synchronous motor.
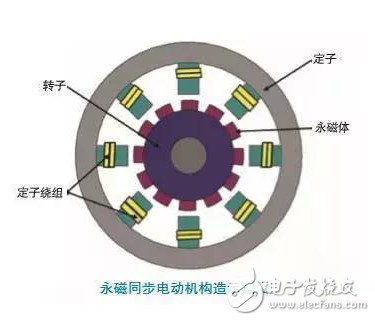
The following are the constructions of GM and Audi's permanent magnet synchronous motors:


Finally, we must also say, what are the characteristics of permanent magnet synchronous motors?
The permanent magnet motor has a higher power/mass ratio, smaller volume and lighter weight. It has larger output torque than other types of motors, and the motor's limit speed and braking performance are also excellent. Therefore, the permanent magnet synchronous motor has become The electric motor with the most applications in electric vehicles today. However, when the permanent magnet material is subjected to vibration, high temperature and overload current, its magnetic permeability may be degraded or demagnetization may occur, which may reduce the performance of the permanent magnet motor. In addition, the rare earth permanent magnet synchronous motor uses rare earth materials, and the manufacturing cost is not stable.
KNB2-63 Miniature Circuit Breaker
KNB2-63 Mini Circuit breakers, also named as the air switch which have a short for arc extinguishing device. It is a switch role, and also is a automatic protection of low-voltage electrical distribution. Its role is equivalent to the combination of switch. Fuse. Thermal Relay and other electrical components. It mainly used for short circuit and overload protection. Generally, According to the poles, mini Circuit breaker can be divided into 1P , 1P+N , 2P, 3P and 4P.
KNB2-63 Miniature Circuit Breaker,Electronics Miniature Circuits Breaker,Automatic Miniature Circuit Breaker,Mini Circuit Breaker
Wenzhou Korlen Electric Appliances Co., Ltd. , https://www.zjaccontactor.com