This article mainly describes how to conduct VR usability testing and how it differs from other platform tests, helping designers of VR products to quickly perform usability testing and improve product quality and experience.
| What Usability Test Is
In simple terms, usability testing is the process of exposing product problems through user testing or expert testing without knowing or wanting to confirm product problems.
For example, a small business started a children's toy store on its own, but didn't know that the shelves were highly inappropriate, so the relatives' children were asked to test enough toys on the shelves. At this point, the toy store is a product. The child is a test object and the height of the shelf is tested.
| What is the significance of doing usability testing?
The significance of usability testing is mainly divided into two aspects:
In terms of users, usability testing can optimize product issues in advance and improve the user experience. For example, when a child participates in a test, there is no way to get a toy on a high shelf to cry. When a small business puts down the shelves, the children are happy to get the toys they want. This is obviously an improvement of the user experience. .
At the product level, the most direct benefits of solving product problems are improved user conversion rates, increased user volume, and profitability. For example, small businesses put their toys on places that children can easily get, take more children, and the turnover naturally goes up.
| What is the difference between VR usability testing and other platform testing?
VR is an emerging medium, so it is unfamiliar to most people, but it is undoubtedly difficult for people engaged in VR-related work to recuperate wasteland. Because of the change of media, the tools, processes and methods corresponding to the design and development have changed along with it. They can no longer use the design of the original PC or mobile terminal, and VR has changed the traditional application of the operating mode and the user's psychology, so for VR For product designers, usability testing is the most direct way to understand user feedback and psychological feelings.
How is the usability test of that VR product different from other application tests?

First of all, it must be stated that all user research focuses on the user, not the platform, so the research methods and procedures of different media are similar, and the usability testing of VR devices is also the same.
For the actual testing process, such as inviting research objects, research room preparation, test attention points, research analysis, etc., VR usability testing is very different from other platform testing.
The difference in the invitation test object:
VR usability testing makes it harder to grasp the scope of test objects. For example, if a shopping app is to be tested for usability, it is sufficient to delineate users who have a shopping experience on the cable and do not bother to consider people who do not have a mobile phone or have no shopping experience. The difference is that VR is not yet a mass consumer device, which will affect the scope of your invitation to test the object. For example, your test object will not be your target user at all, because he will not buy VR devices at all. Then you must be clear about what types of test objects you need to invite.

Differences in test preparation:
1. Consider the size of your laboratory. Because the VR test task may require the test object to move around, such as experiencing a Tilt brush, it is not possible to sit down to complete the space painting. In order to allow the user wearing the glasses to not touch other items, at least a certain amount of experimental space is required. Here we give the size of several common experiments as a reference.
In the living room laboratory (approx. 4m x 4m), the living room experiment is mainly intended to create a sense of home for the user. By simulating the scene in which the user actually uses the product, the user can observe the most realistic and natural test status of the user, but the best method is the user log. Record (another user research method).
One-on-one laboratories (approximately 3m x 3m) are the most common laboratory setups. A user researcher is responsible for testing one user while others are viewing the user through a one-way glass.
Adaptive space (about 4m × 5m), when the usability test task is purely open, there is no user researcher to guide the side, then you need to provide users with their own room for adaptation. This test method is helpful to discover more product problems, but the test process is more difficult to control.

2. Make sure the user is in the sensing area. The VR device has an optimal operating area. When the user leaves the area, the data transmission easily fails and the task cannot be performed. When such a situation occurs in the usability test, inexperienced users will be panic-stricken. They don't know how suddenly the vision is going to be. Is it because of power failure? what should I do? Therefore, it is best to guide through the ground icon before the test, and inform the user of what may happen and solutions.
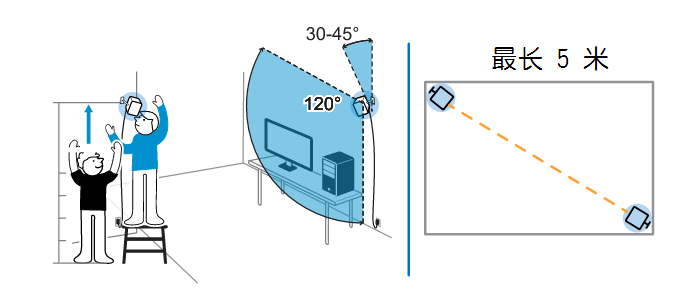
3. Do not let the test instrument interfere with the VR device. This refers to VR helmets that are positioned by infrared sensors. In the usability test lab, the one-way glass observation chamber is more common , and in the VR usability test, this one-way glass causes the infrared light source to repeat, causing position tracking interference, which may affect the usability test process.

4. Need more video cameras. This is to record the user's behavioral actions and expressions from multiple angles. Especially in the virtual environment, the user can easily rotate the body. If there are no cameras in multiple directions, there are many dead angles when reviewing the user's operation records. In order to prevent too much inconvenience for video data, it is recommended to mark the location of the photographic data and set up the main camera position.

5. A screen is needed to synchronize the virtual environment that the user sees. This facilitates the analysis of why users operate this way. For example, if the user repeatedly shakes his head, the virtual environment synchronized with the screen can be combined. The reason may be that there is always a small object looming on the screen, and the user keeps shaking his head to see the small object.

Differences in test notes:
1. Pay attention to user's security . In VR, users can turn head and limbs in different directions and walk in a small area. At this time, it is necessary to pay close attention to the user, whether the user is uncomfortable or potentially harmful due to the design. If there is a potential hazard, the designer should adjust the plan in time. For example, when experiencing a VR parkour game, users easily swing their arms against the wall. (Indicating that the hand was injured many times TT)
2. Focus on user interactions. In virtual reality, the user interacts with the virtual object and space, which is no longer the click operation of the plane device. Therefore, VR's new operating methods need constant attention and exploration, such as whether to allow users to immerse themselves in the virtual environment, whether users can interact with each other without barriers, and so on.
3. Pay attention to the comfort of the user. Because of the immaturity of technology, VR products currently have a lot of comfort issues, such as nausea, image delay, equipment is too heavy, winding or other software or hardware issues. However, many of these problems vary from person to person. Therefore, when analyzing test results, you need to combine different types of users for analysis.
4. Problems with helmets and focal lengths. You may need to help users with helmets and focus adjustments, because most people do not have experience using VR products, so many things you must help him, although this is not the test focus, but it will affect the usability results.
You can try this:
You can write a script to help them bring helmets to make sure they have the helmet properly.
You can use specific evaluation criteria as a test, such as by looking at the text, asking them to tell you if the text is sharp or fuzzy.
5. Longer test time. The user cannot see or hear your voice, so that the test task is not so easy, and it may take longer to test.
However you can do this:
Ensure that the testing process does not depend on interruptions, and that other tests are conducted after completing one phase.
Together with the test subjects, they watch the video and ask about the reason and thoughts of the behavior at that time.
The voice of the researcher can be conveyed to the test subject's earphones, which can help the test run smoothly instead of constantly patting his shoulder: D
| Summary
In general, the VR usability test is more difficult to test than other platforms, and the researcher's personal qualities are even higher. The difficulty of testing mainly focuses on inviting users, setting up a test environment, troubleshooting test conditions, and recording test procedures. The researcher's personal qualities require deeper industry knowledge, such as VR hardware, VR technology, spatial interaction, ergonomics, and neurology.
In addition, there are few research results on VR at home and abroad, most of which focus on the analysis of industry trends and quantitative research on the user market. This phenomenon also shows that the VR market has a great development prospect. It is believed that when VR applications are gradually enriched, related user research will be more comprehensive and in-depth.
references:
Running User Tests for Virtual Reality, Steve Bromley
Virtual Reality User Research, Brian Essex, Ph.D.
VR/AR Innovation Research Report, VRDC
HTC vive User Guide
Lei Feng network (search "Lei Feng Network" public number concerned) : According to the author of this article Liu Pingping, from NetDragon.com.cn.
Specifications:
Mechanical life: More than 50.000 cycles
Electrical life: More than 100,000 cycles
Environment temperature Range: - 25 degrees ~ 85 degrees
Operating Relative Humidity Range: ≦96% RH, +40°C
Features
WIDE APPLICATION
Widely used for various kinds of electrical products, instrument, car, boat, household appliances such as lights, water dispenser, treadmill, coffee pot, speaker, electric car, motorcycle, TV, massage machine etc.
EASY TO INSTALL AND USE
2 PIN on-off Rocker Switch with SPST design, simple installation, freely turn on or off the load which you want to control.
HIGH OPERATING LIFE
Made of high quality polyamide eP(Nylon PA66) material, this sturdy mini boat rocker switch is born for anti-corrosion,anti-acid and high resistant with silver terminals.100,000 times of ON/OFF operating life span.
Small Rocker Switch,Micro Rocker Switch,Single Pole Rocker Switch,Single Rocker Switch
Ningbo Jialin Electronics Co.,Ltd , https://www.donghai-switch.com