This paper discusses the current development of LED distribution photometers, mainly for the analysis and research of instruments based on imaging photometry, using CCD or digital camera as the means of distributed photometric measurement. According to the characteristics of LEDs with half-surface illumination, this study uses the setting of a parabolic reflector to condense and reflect the LED illumination. The LED direction can be converted by a stepping motor at a certain angle to obtain spots at different angular positions, using CCD or It is a digital camera for testing. After obtaining the illuminating spot reflected by the LED, the light distribution curve of the LED can be obtained according to the spot by appropriate image processing.
The luminaire distribution photometer is a large-scale precision optical test equipment, which is an essential equipment for luminaire distribution photometric measurement. The traditional distributed photometer is mainly a mechanical structure, which measures the light intensity distribution of the entire three-dimensional space by mechanically controlling the rotation of the probe. The conventional distributed photometers currently under development mainly have a rotating mirror type distribution photometer. Several types of structures, such as a moving mirror-type distribution photometer and a rotating lamp-type distribution photometer, have been required for the optical and electrical testing of LEDs. They are also the basis for LED testing using conventional photometric methods. In recent years, with the development and maturity of CCD imaging technology, and because of its good visualization effect, simple and convenient, people began to gradually adopt imaging technology for photometric measurement. Currently, it has been used in imaging technology-based luminance meter to assist traditional types. Brightness meter. The research based on the optical intensity distribution of the imaging photometric measurement lamp is still in the research stage because it is more complicated and the precision is difficult to improve. The distributed photometric measurement of luminaires is an important part of quality control in luminaire design and lighting design. Especially with the development of new light sources such as LEDs and emerging lighting technologies, it poses new challenges for luminaire distribution luminosity measurement. Therefore, based on the current development situation and needs, we develop the distribution photometer based on the imaging photometric method for LED light intensity distribution test.
At present, the quality of products in the domestic lighting market is mixed, and a large number of new lamps are flooding into the market every year. The assessment of actual lighting effects is often not evaluated effectively. At present, the distribution of light intensity in domestic measuring lamps adopts a mechanical distribution photometer, which is bulky and expensive, and can only be purchased by a large lighting company or research institute. However, some domestic manufacturers of photometric measuring instruments have good performance, and some aspects can reach international standards and are also adopted by domestic manufacturers. There are also many manufacturers of photometric instruments in the world, and the products are mature, such as Germany. Companies in some countries such as the United States.
In 2005, the imaging measurement device ILMD (Imaging Luminance Measurcment Device) has been introduced to CIE, and a new TC2-59 was established to study the characteristics of ILMD.
Instruments that use imaging technology to measure the light environment have been used in some scientific research experiments and practical applications. Measuring instruments based on the principle of imaging luminosity have great room for development. The LED imaging photometer system studied in this paper is a new type of photometric measurement system, which can collect the light intensity distribution data of the luminaire simply and quickly, and obtain the light distribution curve.
2 test principleIn this paper, imaging photometry is used to solve non-imaging photometric problems, through image processing techniques, combined with photometry and visual science. Calculate and quickly obtain the light distribution curve of the fixture. Figure 1 is a schematic view of the structure of an imaging photometer. Its structure mainly includes parabolic mirrors. Stepper motor, polarizer or soft lens, optical lens set, CCD.CMOS or digital camera. During the measurement, the LED light source to be tested is placed through the bracket at the focus of the curved reflective bowl. The LED light source emits light in the range of 180 ° C. When placed, the direction of the light emitting surface is toward the curved reflective bowl. The light emitted by the LED is reflected by the curved reflective bowl to form a light beam, which is directly irradiated into the optical lens of the CCD.CMOS or digital camera, and automatically determined by the built-in program of the CCD.CMOS or digital camera imaging device to determine if the incident light intensity is too large ( If the threshold value is not determined, the starter motor applies a polarizer or a soft film to the optical path, and adjusts the angle of the polarizer with a motor. If the light intensity value is within the allowable range, no polarization is required in the measurement optical path. Piece or soft film. If CCD or CMOS is used, y (A) filter correction is required. When using a digital camera, the corresponding pixels of the digital camera are mainly corrected. The light beam incident on the CCD.CMOS or digital camera forms a spot on the photosensitive device. The setting program inside the CCD.CMOS or digital camera measures the multiple spot images with a pre-calibrated formula to calculate the light emitted by the LED. The chromaticity of the spatial distribution. Luminance data, LEDs are also controlled by stepper motor, which can achieve ±5 °C and ±10 °C deflection, thus obtaining spots with different deflection angles, so that the distribution of the center intensity of the LED can be corrected.
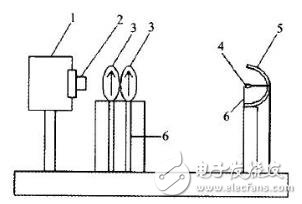
Figure 1 Schematic diagram
After the data is corrected by the visual parameters, it will be sent to the software inherent in the device for format conversion, and finally the LED light distribution curve will be output in the IES format. Figure 2 is a flow chart of the working principle of the imaging acquisition system. First, the imaging acquisition system is scaled, and then the LED emission spot image is collected. By determining whether the overexposure range is exceeded, the system determines whether to increase the polarizer or the soft lens, and proportionally weakens the spot intensity. After the image acquisition system collects the LED emission spot, it is corrected by software calculation to obtain the LED light distribution curve.
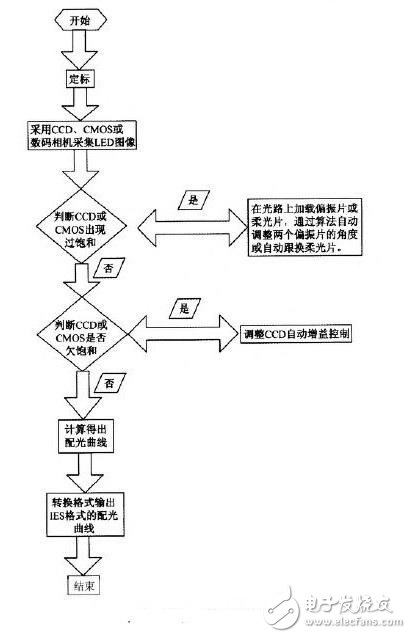
Figure 2 system working principle diagram
3 LED imaging photometer structureThe structure of the LED imaging photometer is shown in Figure 1, and the main part is shown in Figure 3. The photometer mainly includes a parabolic reflector. The LED light source is placed on the bracket. Translucent spot receiving screen and CCD imaging device. The parabolic reflector opening and the focus are in the same plane, and the outer diameter of the receiving screen is the same as the outer diameter of the opening of the parabolic reflector. The size of the opening of the parabola depends on the measurement of the LED luminaire. To ensure that the measured light source is small relative to the test equipment, it can be regarded as a point source. The positional distance of the translucent spot receiving screen is also adjusted according to the test light intensity. By measuring this way, the light intensity will have two attenuations, one for parabolic reflection and one for the receiving screen.
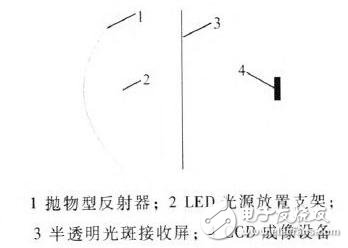
Figure 3 LED imaging photometer planar structure
T Copper Tube Terminals,Non-Insulated Pin-Shaped Naked Terminal,Copper Cable Lugs Terminals,Insulated Fork Cable Spade Terminal
Taixing Longyi Terminals Co.,Ltd. , https://www.longyicopperterminals.com