1. Overview of the development of mobile communication systems
1.1. Global mobile communication industry development and trend insights
With the continuous development of the mobile Internet and the rapid growth of the Internet of Things, mobile broadband technology continues to evolve. The development of mobile broadband technology has stimulated a surge in MBB traffic. In the first half of 2014, the number of global mobile subscriber connections is expected to reach 7 billion, covering more than 96% of the world's population, and the sum of 3G and 4G mobile subscriber connections will reach 2.4 billion, accounting for more than one-third of the global total. . These data indicate that MBB services are growing rapidly.
MBB is booming, and “connections are everywhere†has become the trend of mobile Internet development. This trend indicates that the wireless network will undergo profound changes in the next five years (until 2018), and the MBB business will be transformed into service-oriented and value-focused, focusing on the network TVO (Total Value of Ownership) and building a user-oriented experience. High-quality MBB network with xMbps and coordinated high efficiency anytime, anywhere.
â— MBB business is transforming to focus on service and value, aiming at user experience
In the era of mobile Internet, mobile services are gradually evolving from traditional voice and SMS services to data pipes and capacity services. The voice and SMS services are strongly impacted and eroded by the OTT service (the service that Over The Top operates on the Internet), resulting in the continuous decline in the overall revenue of operators and the need for operators to expand new services. The business complexity of new areas such as enterprise networks requires multi-party cooperation, which leads to the need for operators to open network capabilities. That is, operators provide some network capabilities to third parties in the form of services, and third parties call these services to generate new ones. Application, forming differentiated advantages, ultimately serving enterprises, industries or end users.
Figure 1 MBB business evolution process
To support B2B (Business-to-business to business), B2B2C (business to business to consumer) business, and more flexible and flexible delivery of various applications and open services. It is especially important to build an MBB network for user experience.

Figure 2 survey shows that user experience helps improve user loyalty
â— Mobile network services shift from "voice" to "data"
The rapid development of the mobile Internet has prompted the mobile network system industry chain to shift from voice-centric to data-centric, which greatly impacts the traditional concept of tradition. It is driving the entire industry chain, from operators to equipment vendors, from the core network to the end of the antenna, from content to terminal and other aspects of the transition. A new generation of mobile networks will provide a richer range of services including voice, data, video, multimedia, and a comprehensive range of services. Data traffic in mobile networks has far exceeded voice traffic, and future voices will provide services based on data. Voice will be just a very small form of business in the data business, and the entire mobile network will be a true data network.
â— Mobile networking from “overwrite†to “coverage†+ “capacityâ€
On the network side, operators and their infrastructure providers have begun to realize that traditional mobile communication networks used to provide voice call services over the past 20 years are not comprehensive enough to meet the data-centric future needs. The networking of mobile networks has focused on coverage from the beginning, while at the same time paying attention to the transformation of network data service capacity.
â— Capacity increase, xMbps is the basis for MBB to provide innovative services anytime, anywhere
The service-centric transformation of MBB services and the high-quality user experience need to be based on MBB anytime and anywhere xMbps. This is evidenced by the rapid migration of high-end mobile users to LTE at this stage. It is expected that 2.5 billion users will migrate to the MBB network in the next five years (as shown in the figure below), and the increase in mobile broadband capacity will be the focus of carrier network deployment.

Figure 3 is expected to migrate 2.5 billion users to MBB networks in the next 5 years
â— Collaborative efficiency is the basic appeal of MBB network development
Future network development focuses on network TVO, scalability and openness: on the one hand, virtualize network equipment, realize hardware and software decoupling and flexible resource allocation, so as to quickly respond to market changes and improve business agility; To realize virtualized network services and functions, operators and business innovators and end consumers carrying mobile networks form an open and win-win mobile network ecosystem. However, after decades of rapid development of mobile communications, many operators operate multiple wireless access systems at the same time, and multi-system coexistence will be a long-term process to meet the future "TVO, scalability and openness" application requirements of the network. Multi-network collaboration and efficient deployment have become the basic demands of building MBB networks.
â— Collaborative efficiency is the basic appeal of MBB network development
Future network development focuses on network TVO, scalability and openness: on the one hand, virtualize network equipment, realize hardware and software decoupling and flexible resource allocation, so as to quickly respond to market changes and improve business agility; To realize virtualized network services and functions, operators and business innovators and end consumers carrying mobile networks form an open and win-win mobile network ecosystem. However, after decades of rapid development of mobile communications, many operators operate multiple wireless access systems at the same time, and multi-system coexistence will be a long-term process to meet the future "TVO, scalability and openness" application requirements of the network. Multi-network collaboration and efficient deployment have become the basic demands of building MBB networks.
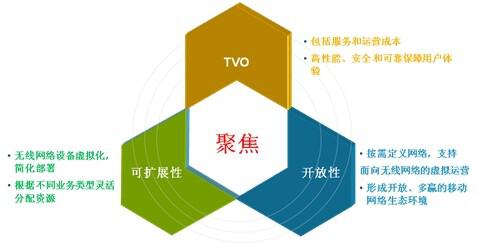
Figure 4 Focus of future MBB network attention
1.2. Development and characteristics of China's mobile communication industry
China's mobile communications industry has experienced rapid development over the past decade. The large-scale user base has laid the foundation for rapid network development. The price reduction and stimulus demand of operators have caused a surge in end users. In 2008, 3G licenses were issued, and China officially entered the era of mobile Internet. Traditional Internet companies also targeted the mobile Internet market. WeChat and Weibo services were widely used. Users of online mobile games continued to grow, and various Internet applications also provided mobile phones. In the client version, the value of the traditional communication industry shifts from pipeline to content, from communication network to the Internet, and from voice service to information service.
In the future, mobile big data traffic demand will continue to grow, and xMbps becomes a common demand for end users anytime, anywhere. In 2013, China's mobile Internet traffic reached 1.29 million TB, 10 times more than the 115,000 TB in 2009. It is expected that domestic mobile data traffic will continue to grow exponentially in the next few years. In order to meet the growing demand for mobile services, domestic operators have also accelerated the pace of LTE construction. The TDD LTE license was issued to the three major operators at the end of 2013. All major manufacturers' products have TDD LTE commercial capabilities. The world's major brand mobile phone manufacturers are actively launching smart terminals supporting TDD LTE. The entire TDD industry is developing well. Of course, with the explosive growth of data traffic, how to do a good job of traffic management and maintain a good balance between meeting user needs and controlling network construction and operation costs is a challenge that domestic operators need to face.
In the era of mobile Internet, which is represented by the rapid development of data services, whether the user experience can be used as the center to enhance the customer experience becomes the focus of competition for operators to compete with the users. Multi-network collaboration and user experience enhancement are the core competitiveness of operators. China's three major carriers have multiple wireless access systems. China Mobile includes GSM, TD-SCDMA and TDD LTE. China Unicom includes GSM, UMTS, LTE TDD and LTE FDD. China Telecom includes CDMA, LTE TDD and LTE FDD. The quality of network collaboration between wireless access systems directly affects the service experience and user satisfaction. Therefore, the evaluation indicators for user experience are established, and more potential problems are discovered, thereby continuously improving the user experience and also building the network of domestic operators. aims.
With the increasing scarcity of wireless spectrum resources, maximizing the use of spectrum resources has become a key element in the construction of MBB networks. According to the current spectrum allocation, China Mobile mainly adopts TDD LTE to build networks, while China Unicom and Telecom will adopt LTE TDD/FDD hybrid networking. Through the integration of FDD LTE and TDD LTE, efficient use of various resources such as frequency is realized.
For the different network status and future target networks, the network construction of the three major operators also has its own characteristics:
â— China Mobile: rapid network construction, taking into account capacity improvement
China Mobile's data traffic has rapidly surpassed voice services, maintaining a compound annual growth rate of nearly 150%. It is expected that in the next few years, with the rapid spread of smart terminals such as smartphones and tablets, and the rapid development of mobile Internet service applications, data services will continue to show an exponential growth trend, and the network resources consumed by data traffic will be voice services. Dozens or even hundreds of times. Faced with the huge impact of this digital flood on wireless networks, reversing the disadvantage of 3G and rapidly building high-bandwidth, high-efficiency, low-cost wireless networks has become an urgent appeal of China Mobile.
In 2013, China Mobile launched TD-LTE network construction in more than 100 cities. Cities such as Beijing, Hangzhou, Guangzhou and Shenzhen have already started commercial trials. It is expected that 500,000 base stations will be deployed by the end of 2014 and will be deployed in 344 cities across the country. Commercially available, the TDD LTE network will be the world's largest TDD LTE network.
In order to achieve the goal of short-term rapid network construction, at this stage, China Mobile mainly adopts F-band upgrade to TDD LTE to deploy LTE network. TD-SCDMA network performance and coverage level have been mature, and site resources are abundant. On this basis, China Mobile deployed TDD LTE mainly for F-band, which eliminated a series of initial network construction problems such as site resource acquisition. However, in the long run, the D-band spectrum resources are abundant, the TDD LTE industry chain is more mature, and TDD LTE wants to become the international mainstream LTE system, which requires a big country like China to play a demonstration role. Therefore, China Mobile’s deployment of TDD LTE in the D-band is also It is imperative.
Flexible application of D-band and F-band for network deployment, network planning in different phases and priorities, is a key strategy for China Mobile to deploy high-quality LTE networks.
â— China Unicom: multi-network collaboration for user experience
At present, China Unicom's 3G network has an advantage in China, and its HSPA+ network rate can reach 42Mbps, which can provide a good user experience. In order to achieve long-term development, China Unicom is also catching up with China Mobile and Telecom LTE deployment while doing a big 3G network. At present, China Unicom has taken the lead in launching 4G network services in 25 cities across the country, and it is expected that 300 cities will be opened by 4G services by the end of the year.
China Unicom currently has GSM900M (954M-960M), GSM1800M (1840M-1850M), WCDMA2100M (2130M-2145M), and TDD LTE (2555M-2575M), and will deploy FDD LTE in the future, facing multi-network coordinated operation and upgrading users. The challenge of experience. It can be expected that 3G as the basic data network, the breadth of coverage and the depth of capacity will remain the competitive advantage of Unicom in the next two years. 4G is positioned as a network providing high-quality data services, FDD LTE covers cities and dense urban areas, and TDD LTE deep coverage The hotspot area meets the needs of high-speed business data and provides users with a better experience.
China Unicom uses the combined competitive advantages of 3G and 4G networks to provide users with a good and seamless business experience.
â— China Telecom: Focus on wide coverage and deep coverage to enhance user experience
For China Telecom, the advantages of CDMA network coverage in the 3G era are obvious. The CDMA 800MHz link loss is small, and a better user experience is obtained with fewer sites. However, LTE is deployed in the 1.8G/2.1G/2.6 high frequency band in the 4G era. The first thing that China Telecom has to solve is the problem of wide coverage and deep coverage of the network.
Based on the target of commercial network, LTE coverage should be at least 98%. After establishing a station with C network 1:1, due to the large station spacing, there are a large number of holes covered. Site patching is a problem that needs to be solved in LTE network construction. For different scenarios such as outdoor, indoor and high-speed rail, China Telecom has introduced a variety of macro stations and small stations to build network forms, reducing the difficulty of site acquisition and solving wide coverage problems. For deep coverage, telecom adopts TDD LTE/FDD LTE hybrid networking mode, FDD seamless coverage eliminates blind spots, TDD absorbs excess traffic in hotspot areas, and introduces CloudBB cloud collaboration, eMBMS and other solutions, covering deep The capacity is thick.
In addition, China Telecom includes CDMA 1X/EV-DO, TDD LTE and FDD LTE multiple wireless access systems, multi-network collaboration, peak rate and edge rate, and commercial VoLTE scale, enabling awareness-oriented networking and user experience enhancement. It will also be the requirements and objectives of China Telecom's network construction and development.
1.3. Summary of the development of mobile communication industry
Building a high-quality MBB network for user experience, xMbps, and high-efficiency anytime and anywhere is a common goal of operators at home and abroad. The development trend of MBB network that connects "everywhere" will lead to profound changes in mobile networks:
â— Wireless network air interface resource convergence
The air interface resources of the wireless network are converged to share the air interface resources of different services and improve the efficiency of the overall air interface. Operators provide differentiated services to meet different business needs, reduce duplication of network construction costs and new site leasing, and support operators to expand new sales models and penetrate into enterprises and industries.
â— Wireless network device virtualization and on-demand network definition
Using high-performance hardware processing and cloud management technologies, it provides operators with flexible, intelligent and scalable automated wireless networks. At the same time, the virtualized network function enables operators to flexibly deploy different OTT services, making the network more valuable.
â— Collaboration between Licensed and Unlicensed spectrum resources
The Unlicensed spectrum is abundant, and nearly 1 GHz of spectrum resources are available, and the 5 GHz band is expected to be distributed over 500 MHz in 2017. Lens spectrum aggregation, broadband and network collaboration technologies enable Licensed+Unlicensed spectrum convergence to enhance the customer experience of the carrier network.
â— Air interface control, bearer separation and collaboration technology support users' borderless experience
The increase of the site is an important means to improve the capacity of the wireless network. In order to meet the 20-fold increase in wireless traffic in 2018, the radio remote modules such as the small station and the AAU will be densely deployed in various hotspot areas. Intensive deployment of the site, the radius of the wireless cell is getting smaller and smaller, which will lead to an increase in inter-cell interference and a decrease in the cell edge capacity. At the same time, the mobility indicator deteriorates and the user experience is reduced. The goal of borderless user experience will promote the rapid development of air interface control and bearer separation and collaborative technology.
â— Network operation and maintenance automation, dealing with the complexity of operation and maintenance brought about by massive stations and massive data
After decades of rapid development of mobile communications, many operators operate multiple wireless networks such as GSM/CDMA/UMTS/LTE at the same time. Multi-spectral and multi-system hybrid networking will be a long-term process; on the other hand, the amount of air interface data The growing number of applications and the small number of small stations have led to a growing network size and complex network operation and maintenance. Therefore, network operation and maintenance automation is one of the requirements for the future development of MBB networks.
â— Energy is accurately placed to build a green energy-saving network
The current energy delivery is extensive, and the base station user signal is received from the base station antenna output to the terminal antenna, and more than 99.9% of the energy is lost in space. In order to reduce the propagation loss of wireless signals in space, the future wireless network will be a green network with precise signal energy. Beamforming, high-order MIMO and other technologies will be widely used.
2. The impact of the development of the mobile communication industry on the base station antenna industry
2.1. Impact of the development of mobile communication technology on the development of base station antennas
The rapid development of mobile communication technology, the change of MBB network structure, and the continuous improvement of the base station antenna technology are mainly manifested in the following aspects:
â— Diversified spectrum resources, insufficient site resources, and multi-frequency ultra-wideband applications are unstoppable
MBB network evolution promotes operators to deploy multi-band and multi-standard wireless access networks. Wireless access equipment is required to support multi-frequency and multi-standard applications and evolution. Multi-frequency antenna applications are undoubted. In the antenna construction, the cost of the antenna itself only accounts for 1/3. The more cost lies in installation, property coordination, and pole, civil construction, and floor rent. The deployment of multi-frequency antennas can avoid repeated installation of antennas and renovation of towers, and reduce roof rent. And antenna follow-up maintenance costs. Take China Mobile as an example, there are GSM 900MHz, 1800MHz, TD-SCDMA 2010MHz~2025MHz A-band, and TDD LTE used 1880MHz~1900MHz F-band and 2600MHz D-band, if single-frequency antenna is used A site needs to deploy multi-faceted antennas, which increases the cost of building stations. It may also be difficult to establish stations due to insufficient space in the sky, and multi-frequency antennas can solve these problems well.
Similarly, with the development of software-defined networks, ultra-wideband RF modules, and scattered carrier aggregation technologies, antenna ultra-wideband technologies continue to evolve.
Select multi-frequency ultra-wideband antennas and have future evolution capability in advance. For operators, you can reserve site resources in advance, save the cost of secondary deployment, avoid the impact of new network optimization on existing networks, and accelerate LTE commercialization. deploy. Take the quad-band antenna (790-960/1710-2690/1710-2170/2490-2690MHz) that can be applied to China Telecom as an example, support CDMA800M/FDD LTE1.8G/TDD LTE2.6G simultaneous deployment, and also have future support for FDD LTE2 .1G capabilities.
â— Capacity demand and daily increase, antennas to MIMO, active and intelligent development
As the key point of network performance in MBB era evolves from satisfying voice coverage to satisfying high-capacity data requirements, antenna focus shifts from coverage to capacity, focusing on overall network performance. Antenna manufacturers need to design antennas around the entire network performance to improve the overall signal-to-noise ratio ( SINR), reducing inter-cell interference.
MIMO (Multi-input Multi-output) is an important way to improve system capacity. As MIMO is widely used in MBB networks, antenna support for MIMO is a basic requirement for network development.
Active Antenna Unit (AAU) is a new RF module form derived from RFU and RRU. The function of the RRU is shifted up, and the function of the antenna is combined. Finally, the vertical array of the antenna and the array of the horizontal array are controlled by the radio frequency multi-channel technology, and the beam of the antenna in the vertical and horizontal directions is flexibly controlled, and the beam is shaped by different beams. The method can improve the coverage quality of the wireless signal and improve the network capacity.
If the antenna is more "smart", when the base station communicates with a certain user, the antenna is automatically adjusted, and the "energy beam" is directly aimed at the user. On the one hand, the signal strength obtained by the user is relatively high, and on the other hand, the antenna should not be The "interrupted" users will not be disturbed, and the result is obviously the most perfect, and the smart antenna is generated. Smart antennas now generally have two technical methods: beam-switched antennas and adaptive array antennas. The beam-switching antenna is generally formed by multiple narrow-beam antennas. Each narrow-beam antenna has a large gain due to its small angle, and the coverage distance is long. It is mostly used in outdoor scenarios, such as some base stations of the TDD LTE system. This smart antenna is deployed. The adaptive array antenna is formed by multiple antennas. When working, it works by combining different antennas to form different antenna lobes, and realizes "virtual antennas" with different directions, angles and gains to adapt to different work. Environment, location of different users, and avoiding unnecessary interference.
â— It is difficult to enter the property, and the antenna will continue to reduce the difficulty of deployment.
With the large-scale increase in the number of sites, site resources are becoming more and more difficult to obtain, and operators have put forward stringent requirements for site selection and simplified construction and installation of base station equipment. When the network performance and coverage requirements are met, the smaller the antenna size and the lighter the weight, the lower the difficulty of antenna deployment and the effective avoidance of visual pollution.
In addition, the general public is more and more sensitive to electromagnetic radiation. A prominent problem in the current construction of mobile base stations is that the site or antenna installation process is blocked by the owner and the site cannot be implemented, even if the site was built before. It is easy to be forced to move, but after the site moves away, mobile users have frequently complained because of poor signal. Site selection and construction is a headache for operators. In this case, it is necessary to perform necessary camouflage on the base station antenna to realize the coordination and unification of the antenna feeder system and the surrounding environment, that is, to beautify the antenna. Depending on the environment, the antenna can be made into a landscaping tree hidden in the trees, or the surface of the cover can be processed into different colors and textures, such as imitation tiles, advertisements, imitation marble textures, etc. For sites with special antenna requirements, According to the actual situation on site, we provide a very personal and well-integrated solution. Beautifying the antenna reduces the public's psychological resistance to the construction of mobile communication base stations and antenna installation, thus reducing the difficulty of antenna deployment.
â— Network maintenance is becoming more and more complex, and the maintenance of the antenna is required.
The network scale is becoming larger and larger, the network operation and maintenance is extremely complicated, the introduction of SON (Self-organizing Network) solution and the requirement of reducing the overall network operation and maintenance cost make the remote maintenance of the antenna an inevitable choice for the MBB network. Antenna remote maintenance includes features such as remote ESC and intelligent weight management.
The remote ESC antenna can adjust the beam downtilt angle of the antenna by controlling the operation of the remote tonal unit (RCU) by remote operation in the network management center. Traditional remote ESC antennas have gradually evolved into plug-and-play ESC antennas due to difficulties in installation, low maintenance efficiency, and poor reliability. Plug and Play ESC, which is built-in to minimize the number of external ESC components and cable required for remote ESC, while eliminating antenna calibration and configuration data loading, thereby improving antenna installation and Operation and maintenance efficiency, improve reliability, and reduce operator operation and maintenance costs.
TDD LTE antenna weight setting requires manual field configuration, low efficiency, large workload, and it is difficult to ensure the accuracy of weight configuration, and intelligent management of weights becomes the operator's appeal. The weight intelligent management stores the weight information of the antenna inside the antenna. After the station is opened, the base station equipment automatically reads the weight and the configuration weight from the antenna to realize the automatic management of the antenna weight.
The remote adjustment of the horizontal direction of the antenna and the automatic detection of coverage holes and early warnings in cooperation with the base station are also research topics for improving the maintainability of the antenna.
2.2. Summary of the development direction of base station antennas
Mobile operators have difficulty in site selection, public attention to visual pollution and electromagnetic pollution, rapid development of MBB to promote the number and density of base stations, and exploration of 5G technology... Base station antennas continue to develop with the rapid development of mobile communication technologies. :
â— Multi-frequency and broadband
Base station antennas evolve to multi-frequency and ultra-wideband, make full use of site resources, simplify site installation, reduce the difficulty of property coordination, and reduce comprehensive investment.
â— Light and thin
The antenna is developed to be lighter and thinner, ensuring the performance of the antenna while increasing the frequency band without increasing the size, thereby reducing the difficulty of property access, avoiding the cost input caused by the tower pole pole transformation due to the large wind resistance, and accelerating the deployment of the LTE network.
â— Beautify
For different scenarios, different camouflage of the mobile antenna is made, and the coordination and unification of the antenna feeder system and the surrounding environment are sought to be achieved, and the camouflage material is considered to have no significant influence on the coverage performance of the antenna. This can not only meet the requirements of network construction, but also coordinate with the surrounding environment to achieve the best of both worlds.
â— MIMO
With the development of mobile communication technologies, supporting high-order MIMO and flexible configuration of MIMO will be the basic characteristics of the antenna. 4x4 MIMO antennas have been widely used, and high-order MIMO antenna technology will also be applied with the development of future MBB services. In addition, under the demand of the antenna once deployed, the antenna also needs to support flexible MIMO configuration between different antenna ports in consideration of future network evolution.
â— Activeization
Adopting the transceiver separation and digital active antenna AAU, the beam can be controlled in real time, and it can adapt to more flexible radio resource management, improve the performance of the communication base station, utilize spectrum resources more effectively, and achieve higher traffic, lower cost, energy saving and emission reduction. Requirements.
â— Intelligent
The smart antenna technology utilizes the difference in signal space characteristics between mobile users, and receives and transmits multiple mobile user signals on the same channel through array antenna technology without mutual interference, so that the utilization of the radio spectrum and the transmission of signals are more effective. Smart antennas can be used to meet the quality of service and expand network capacity without increasing system complexity.
Smart antennas are very tightly integrated with system algorithms, and the algorithms for systems and antennas are beyond the scope of traditional antenna design to some extent. It is a cross-research field between hardware and software, which will be a very important for antenna manufacturers. Big challenge.
â— Remotely maintainable
Remote ESC is a prelude to the improvement of antenna maintainability, antenna horizontal azimuth remote control, RAE technology, and base station collaborative coverage hole detection and early warning, etc. Various maintenance features will be researched, developed and applied, and finally the site will be upgraded. Operation and maintenance efficiency reduces operator operation and maintenance costs.
â— High quality and long-term reliability
High-quality antennas for data and capacity are one of the important guarantees for the performance of the entire wireless network. In the 2G era, voice services are dominant, and voice is a low-rate service feature. The coded modulation mode of the voice service in the air interface of the wireless network is mainly a low-rate code modulation method with good error correction capability, such as QPSK/BPSK. Such low-rate modulation methods have good wireless air interface immunity, so the quality requirements for wireless air interface channels are lower. In the 4G era, data services are the mainstay, and wireless air interface QAM modulation has become the mainstream modulation method for providing high-speed services. This type of modulation has higher requirements on the channel quality of the wireless air interface, and the channel quality of the wireless air interface has a huge impact on the data traffic. Good wireless air interface channel quality, compared with wireless air interface with serious interference, the data traffic flow is N times different. At the same time, long-term reliable wireless air interface quality has become a must. Therefore, in the 4G era, antennas have a serious impact on the quality of wireless air ports, and their high quality and long-term reliability have higher requirements. The status of such devices in the network is more important than in the past.
â— Welcome to 5G: 3D-MIMO, beam intelligent shaping
One of the important research directions of 5G technology, base station antenna technology will undergo passive-to-active, two-dimensional (2D) to three-dimensional (3D), high-order MIMO to large-scale array development, and it is expected to achieve spectrum efficiency improvement. Ten times or even higher. In the future, with the introduction of active antenna arrays, the number of cooperative antennas that can be supported by the base station side will reach 128; 2D antenna arrays will be expanded into 3D antenna arrays to form a novel 3D-MIMO technology, which supports multi-user beam intelligent shaping and reduces inter-user interference. Combined with high-band millimeter wave technology, wireless signal coverage performance will be further improved.
Higher frequency bands, 3D-MIMO, beam smart shaping and other 5G elements will promote the further development of base station antenna technology.
Emergency LED drivers are designed specifically for light fixtures . These emergency backup drivers regulate the power supplied to the LED fixture the same way normal drivers do , but they operate off of a battery instead of line voltage . Because they operate off a battery the light output isn't as bright as the fixture normally would produce , but it will be just enough in an emergency situations . Most of our emergency LED drivers have a maximum emergency operation time of 120 minutes .
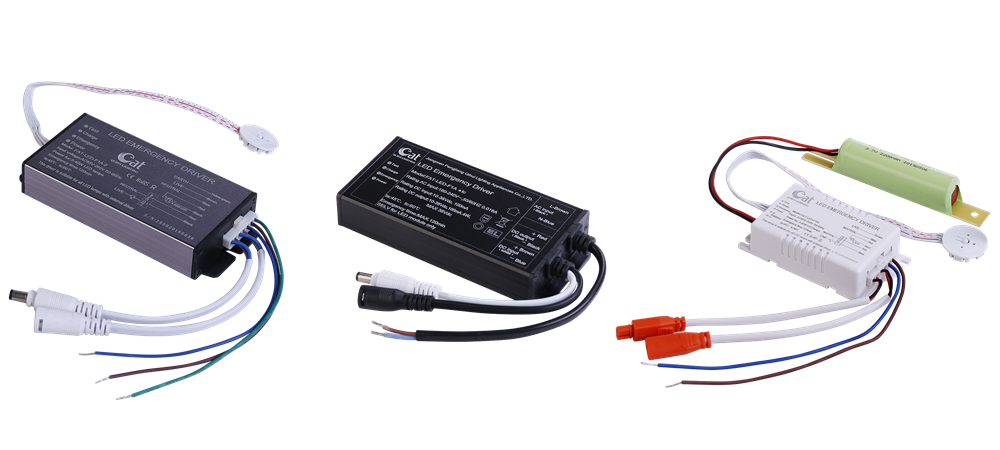

Emergency Inverter Kit,Battery Backup LED Lighting,LED Emergency Light Module
Jiangmen City Pengjiang District Qihui Lighting Electrical Appliances Co., Ltd , https://www.qihuilights.com