Most people believe that high-brightness LEDs (HBLEDs) will be the ultimate sensible choice for lighting. Manufacturers of HBLEDs have significantly increased the lumens per watt of their products and continually improved the energy efficiency of their products, which has made HBLEDs more and more popular. I believe that soon after, the lumens per watt of LED will greatly exceed the current level of fluorescent lamps.
LED lighting was first used primarily in the replacement of low-voltage spotlights and track lights. This includes replacing the original standard size fixtures such as MR16, PAR20, PAR25, PAR30 and PAR38. National Semiconductor (NS) has provided a variety of solutions for beautifying LEDs for these applications, including the LM342X and LM340X family of LED drivers. But no matter how these LEDs are driven, they all face a common problem: how to dissipate heat. For these small package sizes, heat sinks that rely solely on the free flow of air are often insufficient. This necessitates designers to consider adding certain fixtures that force air flow. For devices of this size, the most common method is to use a DC fan or use the Nuventix Synjet as a more sophisticated and durable solution. Fans tend to be more economical and can operate on 5V or 12V DC voltages, but they are not easily embedded in lighting fixtures, and the life of the fans is tens of thousands of hours. Synjet, on the other hand, is specifically designed for the installation of these lighting fixtures. It operates at 5V DC and can last up to 100,000 hours.
The standard input for these systems can be DC or AC systems. 12V and 24V AC systems have been widely used in low-voltage lighting systems, while 12V and 24V DC systems are gradually being promoted and increasingly popular. Since 12V systems are very common, it is not difficult to design and drive a 5V cooling system. But because of the existence of so many systems, the input voltage distribution range will be very wide, especially for AC input, the ideal situation is to have a solution to convert a wide range of input voltage, and then provide 5V voltage, while It takes up very little space and can be easily embedded in the lighting fixture. Fortunately for the small device, the LM2842 can achieve the above requirements well, similar models of the LM2841 can do the same.
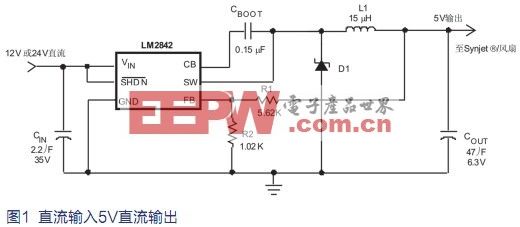
The DC input system can be used as a transformer to convert a wide input voltage directly to 5V, which is the easiest and simplest solution. Typical solutions include fans and Synjet required drive currents ranging from 100 to 600 mA. The LM2841 is capable of delivering 300mA to a small cooling system, and the LM2842 is capable of delivering up to 600mA to a larger, more powerful cooling system. The LM2842 is shown in Figure 1 with an input voltage of 12V DC or 24V DC to provide the necessary 5V. The entire solution can deliver up to 600mA, but only takes up about 1/4 of the PCB (printed circuit board) area, making it easy to embed in any improved device. Based on the exact same design, the LM2841 is designed for lower current applications while allowing the use of small physical inductors for smaller footprints.
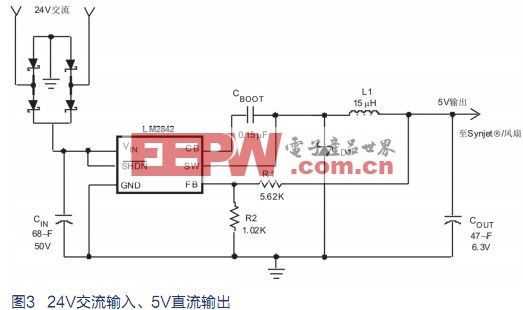
However, as mentioned above, many 12V AC and 24V AC systems are being widely used, and it is hoped that they will continue to function after improvements, rather than being completely replaced with more advanced DC systems. This means that a wide range of input voltages must be considered in the design. To achieve this, a bridge rectifier and a large number of input capacitors can be simply used to form the original AC-DC rectifier. Taking into account the line tolerance, the peak voltage that the 24V AC system can provide will be 40V. However, if the input capacitance is minimized, the input voltage will drop to 10~12V. The LM2841 and LM2842 allow the input voltage to vary over a wide range, providing adequate power rejection and ensuring that the output voltage is accurately stabilized at 5V. Figure 2 and Figure 3 show the circuit diagrams for the 12V AC and 24V AC systems, respectively.
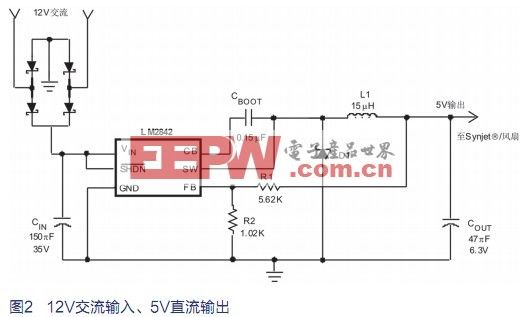
There are a few points to note here. The 24V AC input has a high RMS voltage, which makes the current of the LM2842 small. It also has a higher peak. For these reasons, the LM2842 can use a smaller input capacitor to maintain a reasonable operating input voltage. It should also be noted that the circuits in Figures 2 and 3 are designed for a complete output voltage of 600mA. Because of this, it is obvious that if the cooling system uses a lower current, then the smaller input capacitance can be used to further reduce the circuit size. For example, if the LM2842 is replaced with the LM2841, the maximum output current will be 300mA, so the input capacitance can be halved.
If you have the right driver tools, thermal management of LEDs will no longer be a problem.
Led Spot Light,Led Spotlight Bulbs,Spotlight Lighting,Led Spot Lamps
Shenyang Haimeng Lighting Co. , http://www.hmwled.com