The Internet of Things hopes to connect people and things, things and things through communication technology. Short-distance communication technology is generally used in LAN communication scenarios such as smart home and industrial data collection, but long-distance communication technology is required for wide-range and long-distance connections. LPWAN technology is officially a long-distance wireless communication technology that meets the needs of the Internet of Things.
When it comes to long-distance wireless communication, you may have questions about mobile cellular communication technology? Indeed, at present, global telecom operators have built mobile cellular networks covering the whole world. However, cellular networks such as 2G, 3G, and 4G have wide coverage, but IoT devices based on mobile cellular communication technologies have disadvantages such as high power consumption and high cost. The mobile cellular communication technology was originally designed for human-to-human communication. According to an authoritative analysis report, the current global connection of objects and objects actually carried on the mobile cellular network accounts for only 6% of the total number of connections. The main reason for such a low proportion is that the current mobile cellular network has insufficient carrying capacity to support the connection of objects. To learn about cellular communication technologies and the Internet of Things, check out "Technology Development and Internet of Things from a Technical Perspective"
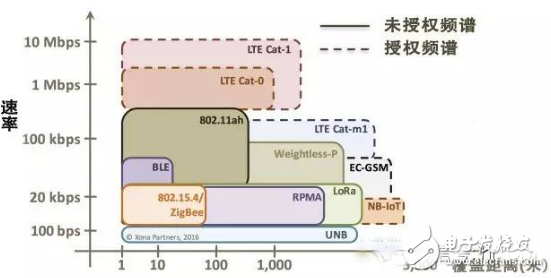
LPWAN (Low Power Wide Area Network), a low-power wide-area network designed for low-bandwidth, low-power, long-distance, high-connection IoT applications.
LPWA can be divided into two categories : one is LoRa, SigFox and other technologies working on unlicensed spectrum; the other is 2/3/4G cellular communication technologies supported by 3GPP, such as EC-GSM and LTE, operating under licensed spectrum. Cat-m, NB-IoT, etc.
Next, the electronic enthusiasts will bring you two kinds of technical details of LPWA:
LoRa
LoRa is not an unfamiliar technology, it is currently one of the most widely used LPWAN network technologies, and the agreement comes from SemTech, which plans to gradually license other source files.
The main features of LoRa wireless technology:
Long distance: 1 ~ 20 km
Number of nodes: 10,000 or even millions
Battery life: 3~10 years
Data rate 0.3~50kbps
As a wireless technology, LoRa is based on the Sub-GHz frequency band, making it easier to communicate over long distances with lower power consumption, and can be powered by battery or other energy harvesting. Lower data rates also extend battery life and increase network capacity. The LoRa signal is also very penetrating to the building. These technical features of LoRa are more suitable for low-cost large-scale IoT deployment.
In the city, the general wireless distance ranges from 1 to 2 kilometers. In the suburbs or open areas, the wireless distance will be further. The network deployment topology layout can be designed according to the specific application and scenario. LoRa is suitable for low communication frequency and small amount of data. How many nodes or terminal devices a gateway can connect to, according to Semtech's official explanation: an SX1301 has 8 channels, and the LoRaWAN protocol can accept about 1.5 million packets of data per day. If your application sends a packet every hour, an SX1301 gateway can handle approximately 62,500 end devices.
LoRa application
From the current LoRa application situation, there are mainly data transparent transmission and LoRaWAN protocol application. At present, LoRa is still used as data transmission. Because the threshold of gateway technology and development is relatively high, the application of LoRaWAN protocol networking is still relatively small.
From the aspect of LoRa network application, there are big nets and small nets. Small network refers to the user's own node, gateway and server, which is a system network. Large network is a large-scale basic network deployment, just like China Mobile's communication network. From the perspective of LoRa industry practitioners, many telecom operators are also involved. With the increase of LoRa devices and networks, spectrum interference exists between each other, which puts forward requirements for the allocation and management of communication spectrum, and requires a unified coordination management mechanism and a large network management.
Several issues to consider for LoRa applications:
Distance or range
Power or power consumption
Number of nodes
Application scenario
cost
Compared with other wireless technologies (such as Sigfox, NB-IOT, etc.), the LoRa industry chain is relatively mature and commercialized earlier. Previously, Microchip announced the launch of LoRa-enabled communication modules, and the French Bouygues telecom operator announced that it will build a new LoRa network. Semtech also works with a number of semiconductor companies (such as ST, Microchip, etc.) to provide chip-level solutions that enable customers to acquire LoRa products and adopt LoRa wireless technology and implement IoT applications.
In addition, the LoRa Alliance was established at the beginning of this year and is the first industry alliance in the LPWAN field, aiming to promote the popularity of LoRa by building an ecosystem.
SigFox
SigFox is also a LPWAN network technology that is faster to commercialize. It uses ultra-narrowband technology, which allows network devices to consume 50 microwatts of power for bidirectional one-way communication or 100 microwatts. In comparison, mobile phone communication requires about 5000 microwatts. This means that the maximum length of each message on a device connected to the Sigfox network is approximately 12 bytes, and no more than 140 messages can be sent per device per day. Turning to coverage, the company wants their network to cover up to 1,000 kilometers and each base station can handle one million objects.
The agreement is owned by SigFox and its founder is French entrepreneur Ludovic Le Moan, which creates a low-cost, low-cost wireless IoT private network.
Sigfox network construction action this year
In February 2016, SigFox began to build a network in the Czech Republic. The project is called SimpleCell. After one and a half months of deployment, the network covered more than 3,300 cities and municipalities, exceeding the original plan to cover half of the 6,245 locations. In cooperation with T-Mobile, more than 60 SimpleCell base stations have been built and are scheduled to be deployed in all regions in May this year.
In April 2016, SigFox teamed up with Thinxtra to deploy an IoT network in Australia and New Zealand to provide a global, cost-effective, energy-efficient communications solution for thousands of sensors to be networked. Through this collaboration, SigFox has also extended the reach of deploying a global network to the Asia-Pacific region, setting a milestone for the company to deploy its own network in the Asia-Pacific region, marking the company's launch of services in more than 30 countries in 2016. One step.
Sigfox has established partnerships with many manufacturers in the industry chain, such as module manufacturers, device manufacturers, chip manufacturers, and IoT platform providers, such as:
Collaborate with Core Labs to combine the lab's EZRadioPRO wireless transceiver with UNB technology;
Cooperated with Atmel in the remote IoT connection field, passed the SIGFOXReadyTM certified ATA8520 device, and is the first system-on-a-chip (SoC) solution to pass this certification;
Work with TI to create cost-effective, remote, low-power IoT connectivity, enabling TI's CC1120 Sub-1GHz RF transceivers to provide the widest range of connectivity and robust immunity to interference with UNB technology;
The first site was launched in cooperation with infrastructure provider Arqiva.
Guangzhou Yunge Tianhong Electronic Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.e-cigarettesfactory.com