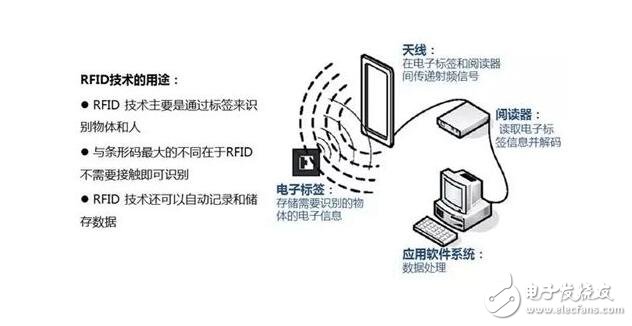
RFID radio frequency identification is a non-contact automatic identification technology, and its basic principle is electromagnetic theory. It automatically recognizes the target object and acquires relevant data through the RF signal, and the identification work can work in various harsh environments without manual intervention. RFID technology can recognize high-speed moving objects and recognize multiple labels at the same time, which is quick and easy to operate.
Accenture's chief scientist Ferguson believes that RFID is a breakthrough technology: 'First, it can identify a single very specific object, instead of identifying only one type of object like a barcode; second, it uses radio frequency, can Data is read through external materials, and the barcode must be read by laser. Third, multiple objects can be read at the same time, and the barcodes can only be read one by one. In addition, the amount of information stored is also very large.

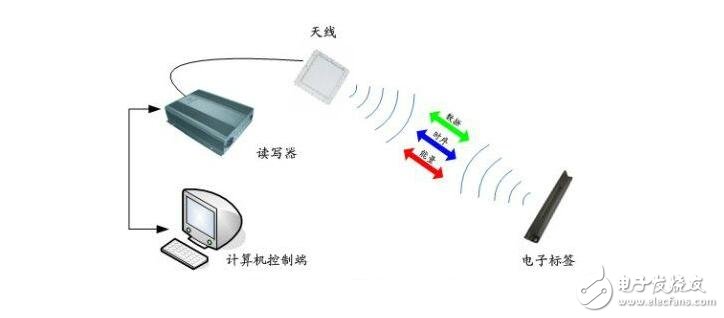
The most basic RFID system consists of three parts: electronic tags, readers and computer networks.
(1) Electronic tag (Tag): The electronic tag contains an electronic chip and an antenna. The antenna transmits RF signals between the tag and the reader. The electronic chip stores data of the object, and the antenna is used to transmit and receive radio waves.
Electronic tags are classified into passive electronic tags, active electronic tags and semi-active electronic tags according to the power supply mode:
Passive electronic tag: There is no battery inside the tag. The working energy is provided by the electromagnetic field emitted by the reader. It is light in weight, small in size, long in life and low in cost. It can be made into various cards. It is the most popular electronic tag form. . The recognition distance is smaller than the active system, generally a few meters to a dozen meters, and requires a larger reader transmit power.
Active electronic tag: powered by the battery inside the tag, does not require the reader to provide energy to start, the tag can actively emit electromagnetic signals, the recognition distance is long, usually up to tens of meters or even hundreds of meters, the disadvantage is high cost and long life Limited, and not easy to make a thin card.
Semi-active electronic tag: There is a battery inside, but the battery only supplies power to the internal circuit of the tag, and does not actively transmit signals. The energy transmission mode is similar to that of the passive system, so its working life is much longer than that of the general active system tag.
(2) Reader: A device that reads and writes electronic tags using radio frequency technology. The reader receives the data information of the electronic tag and transmits it to the external host.
(3) Computer: The reader connects to the computer network through a standard interface, and the computer network performs the functions of data processing, transmission, and communication.
How RFID works:The basic model of the RFID system is shown in the figure below. Among them, the electronic tag is also called the radio frequency tag, the transponder, and the data carrier; the reader is also called the reading device, the scanner, the communication device, and the reader/writer (depending on whether the electronic tag can wirelessly rewrite the data). The space (contactless) coupling of the RF signal is realized between the electronic tag and the reader through the coupling component, and in the coupling channel, energy transfer and data exchange are realized according to the timing relationship.
The basic working process of the system is: the reader transmits a certain frequency of the radio frequency signal through the transmitting antenna, and when the radio frequency card enters the working area of ​​the transmitting antenna, an induced current is generated, and the energy obtained by the radio frequency card is activated; the radio frequency card transmits the information such as its own code through the card. The antenna is sent out; the receiving antenna of the system receives the carrier signal sent from the RF card, and transmits it to the reader through the antenna adjuster, and the reader demodulates and decodes the received signal and sends it to the background main system for related processing; the main system According to the logic operation, the legality of the card is judged, corresponding processing and control are performed for different settings, and a command signal is issued to control the action of the actuator.
There are two types of coupling of RF signals that occur between the reader and the electronic tag.
(1) Inductive coupling. The transformer model is coupled by a spatial high-frequency alternating magnetic field, based on the law of electromagnetic induction, as shown in Figure A on the right. The inductive coupling method is generally suitable for short-range radio frequency identification systems operating at medium and low frequencies. Typical operating frequencies are: 125kHz, 225kHz, and 13.56MHz. The recognition action distance is less than 1m, and the typical action distance is 10-20cra.
(2) Electromagnetic backscatter coupling: The radar principle model, the electromagnetic wave emitted, hits the target and reflects back, and carries back the target information, based on the spatial propagation law of the electromagnetic wave, as shown in Figure B. The electromagnetic backscatter coupling method is generally suitable for long-range radio frequency identification systems operating at high frequencies and microwaves. Typical operating frequencies are: 433MHz, 915MHz, 2.45GHz, 5.8GHz. The recognition action distance is greater than 1m, and the typical action distance is 3-1m.

The basic working principle of RFID technology is not complicated: after the tag enters the magnetic field, it receives the RF signal from the reader, and sends the product information (passive tag or passive tag) stored in the chip by the energy obtained by the induced current, or by The tag actively sends a signal of a certain frequency (AcTIve Tag, active tag or active tag), and the reader reads the information and decodes it, and sends it to the central information system for data processing.
A complete RFID system consists of three parts: the reader and the electronic tag, the so-called transponder and application software system. The working principle is that the Reader emits a specific frequency of radio wave energy to drive the circuit. The internal data is sent out, and the Reader receives the interpretation data in sequence, and sends it to the application for corresponding processing. In terms of communication and energy sensing between the RFID card reader and the electronic tag, it can be roughly divided into two types: inductive coupling and backscatter coupling. Generally, the low-frequency RFID mostly adopts the first type, and the higher frequency mostly adopts the second method.
The reader can be a read or read/write device depending on the structure and technology used, and is an RFID system information control and processing center. The reader usually consists of a coupling module, a transceiver module, a control module, and an interface unit. The half-duplex communication is generally used for information exchange between the reader and the transponder, while the reader provides energy and timing by coupling to the passive transponder. In practical applications, management functions such as collection, processing, and remote transmission of object identification information can be further implemented through Ethernet or WLAN. The transponder is the information carrier of the RFID system, and the transponder is mostly composed of a coupling element (coil, microstrip antenna, etc.) and a microchip to form a passive unit.

At present, RFID products are defined to have different operating frequencies in the frequency range of low frequency, high frequency and ultra high frequency, and RFID products of different frequency bands have different characteristics. The sensors are available in both passive and active modes.
First, low frequency (from 125KHz to 134KHz)
characteristic:
1. The general operating frequency of the sensor operating at low frequencies is from 120KHz to 134KHz, and the operating frequency of TI (Texas Instruments) is 134.2KHz. The wavelength of this band is about 2500m.
2. In addition to the influence of metallic materials, the general low frequency can pass through the material of any material without reducing its reading distance.
3. Readers working at low frequencies do not have any special licensing restrictions worldwide.
4. Low frequency products come in different packages. Good packaging is too expensive, but has a lifespan of more than 10 years.
5. Although the magnetic field region of this frequency drops rapidly, a relatively uniform read/write area can be produced.
6. Compared with RFID products in other frequency bands, the data transmission rate of this frequency band is relatively slow.
7. The price of the sensor is relatively expensive compared to other frequency bands.
Second, high frequency (working frequency is 13.56MHz)
characteristic:
1. The operating frequency is 13.56MHz, and the wavelength of this frequency is about 22m.
2. In addition to metallic materials, the wavelength of this frequency can pass through most materials, but tends to reduce the reading distance. The sensor needs to be some distance away from the metal.
3. The band is recognized globally and there are no special restrictions.
4. The sensor is usually in the form of an electronic tag.
5. Although the magnetic field region of this frequency drops rapidly, it can produce a relatively uniform read/write area.
6. The system is anti-collision and can read multiple electronic tags at the same time.
7. Some data information can be written to the tag.
8. The data transfer rate is faster than the low frequency, and the price is not very expensive.
Third, UHF (working frequency is between 860MHz and 960MHz)
characteristic:
1. In this band, the global definition is not the same - Europe and parts of Asia define a frequency of 868MHz, North America defines a frequency band between 902 and 905MHz, and the frequency band defined in Japan is between 950 and 956. The wavelength of this band is about 30cm.
2. At present, the power output of this band is currently defined uniformly (defined as 4W in the United States and 500mW in Europe). It is possible that the European limit will rise to 2W EIRP (effective isotropic radiated power).
3. Radio waves in the UHF band cannot pass many materials, especially suspended particulate matter such as water, dust, and fog. Compared to high-frequency electronic tags, the electronic tags in this band do not need to be separated from the metal.
4. The antennas of electronic tags are generally strips and labels. The antenna is available in both linear and circular polarization to meet the needs of different applications.
5. This band has a good read range, but it is difficult to define the read area.
6. It has a high data transfer rate and can read a large number of electronic tags in a short time.
Active RFID technology (2.45GHz, 5.8G)
Active RFID has the characteristics of low transmission power, long communication distance, large amount of transmitted data, high reliability and good compatibility. Compared with passive RFID, the technical advantage is very obvious. It is widely used in highway toll, port cargo management and other applications.
Al2O3 Ceramic Ring, High Purity Ceramic Ring, 99% Aluminum Ceramic Ring
Yixing Guangming Special Ceramics Co.,Ltd , https://www.yxgmtc.com