Digital telecommunications is a communication method in which a digital signal is used as a carrier to transmit a message, or a digital signal is used to digitally modulate a carrier. It can transmit digital signals such as telegrams and digital data, as well as analog signals such as voiced speech and images.
Data communication is a new communication method that combines communication technology and computer technology. To transmit information between two places, there must be a transmission channel, and there are wired data communication and wireless data communication depending on the transmission medium. However, they all connect the data terminal with the computer through the transmission channel, so that the data terminals in different places realize the sharing of software, hardware and information resources.
Five basic data communication systems Offline data transmission is the simple transfer of data using a telephone or similar link, excluding computer systems. The devices used at both ends of such a link are not part of the computer, or at least not immediately provide data to the computer for processing, ie the data is offline when sent or received. This type of data communication is relatively cheap and simple. The term remote batching applies to a method that employs data communication techniques to make the input and output of data geographically remote from the computer that processes them in a batch mode. Online data collection refers to the method of using data communication technology to provide the computer with the input data that has just been generated. The data is then stored in a computer (such as a disk) and processed at predetermined intervals or as needed.
The inquiry-response system, as its name suggests, provides users with the ability to extract information from a computer. The inquiry function is passive. That is, it does not modify the stored information. The question can be very simple, for example: "Retrieving a record with an employee number of 1234" can also be complicated. Such systems may use terminals that produce hard copy and/or visual display. A real-time system is a system in which a computer system acquires and processes information in a dynamic situation so that the computer can take actions to affect an event that is occurring (such as in a process control application) or can be accurately stored in the computer. And constantly updated information to influence people (operators), such as in pre-sale systems.
1. Principles of Data Communication--IntroductionData communication is a new communication method that combines communication technology and computer technology. Its communication method refers to the working form and signal transmission mode between two or more parties of communication. If there is a transmission channel to transmit information between the two places, there is a distinction between wired data communication and wireless data communication depending on the transmission medium. However, they all connect the data terminal with the computer through the transmission channel, so that the data terminals in different places realize the sharing of software, hardware and information resources.

A complete data communication system generally consists of the following components: data terminal equipment, communication controller, communication channel, and data communication equipment, as shown in the following figure.
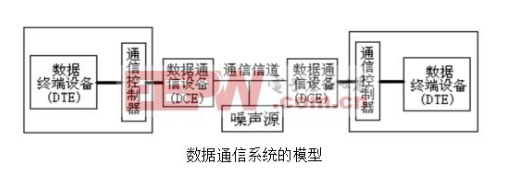
Data Terminal Equipment----English name is Data Terminal Equipment, referred to as DTE, which is the generator and user of data. It controls the communication function according to the protocol. The most commonly used data terminal equipment is the microcomputer in the network.
Communication Controller----It can receive information from multiple data terminal devices and convert information format in addition to operations such as connection, monitoring and teardown of communication status.
Communication channel - it is the channel through which information is transmitted between data communication devices. Such as analog communication channels such as telephone lines, dedicated digital communication channels, broadband cables, and optical fibers.
Data communication equipment----English name is Data Communication Equipment, referred to as DCE, its function is to convert the data provided by the communication controller into a signal form suitable for the communication channel requirements, to ensure the transmission quality to the utmost.
3. Principle of data communication - communication processData is transmitted over the communication line. In general, data communication from a source node to a destination node requires the transfer of several intermediate nodes. Common switching technologies are circuit switching, message switching, and packet switching. The circuit is taken as an example to introduce its principle.
Three processes of circuit switching:
(1) Circuit establishment: Before transmitting any data, an end-to-end circuit must be established through the call process. If the H1 station is to be connected to the H3 station, it is typical that the A node selects the circuit through the B node and tells B that it also needs to connect to the C node; B calls C again to establish the circuit BC. Finally, node C completes the connection to the H3 station. Thus there is a dedicated circuit ABC between A and C.
(2) Data transmission: After the circuit ABC is established, data can be sent from A to B, and then B to C; C can also send data to A via B. The established circuit must remain connected throughout the entire data transfer process.
(3) Circuit removal: After the data transmission is completed, a demolition request is issued by one party (A or C), and then removed to the other node node by section.

The main technical indicators of data communication are parameters that measure the validity and reliability of data transmission. The effectiveness is primarily measured by the data transmission data rate, modulation rate, transmission delay, channel bandwidth, and channel capacity. The technical indicators of commonly used data communication are as follows:
(1) Channel bandwidth: The frequency range over which a channel can transmit signals without distortion. When transmitting analog signals, the unit is Hertz (HZ). When transmitting digital signals, the unit is bits per second, expressed in bits per second (bit/s), abbreviated as bps.
(2) Data transmission rate (bps): The data transmission rate refers to the maximum number of bits that a channel can transmit in a unit of time. The bandwidth of a local area network is generally 10 Mbps, 100 Mbps, and 1000 Mbps, and the bandwidth of a wide area network is generally 64 Kbps, 2 Mbps, 155 Mbps, 2.5 Gbps, and the like.
(3) Error rate/bit error rate: An indicator describing the quality of a channel or data communication system. Refers to the ratio of the total number of transmitted bits on the channel to the number of erroneous bits in the normal operation of the data system.
(4) Transmission delay: refers to the phenomenon that the system information has different degrees of delay or lag in the transmission process due to various reasons.

The information transmitted in the computer network is digital data, the communication between the computers is the data communication method, and the data communication is the communication method combining the computer and the communication line. According to the allowed transmission direction, the data communication method can be divided into three modes: simplex communication, half-duplex communication, and duplex communication.
Data communication transmission methodParallel transmission
Parallel transmission refers to the simultaneous transmission of data on multiple parallel channels in groups. It is common to transfer several binary codes of a character code on several parallel tracks. For example, a character of 8 units of code can be transmitted in parallel with 8 channels, and one character is transmitted at a time. Therefore, there is no synchronization problem of characters in both the receiving and transmitting sides, and it is not necessary to add a "start", "stop" signal or other signals to achieve The synchronization of the characters on both the receiving and sending sides is a major advantage of parallel transmission. However, parallel transmissions must have parallel channels, which imposes limitations on the device or implementation conditions.
Serial transmission
Serial transmission is a method in which a binary code constituting a character is transmitted bit by bit in chronological order on a channel in units of bits (symbols). Send by bit, receive bit by bit, and also confirm the characters, so take synchronization measures. Although the speed is slow, but only one transmission channel, the investment is small, easy to implement, is the main transmission method used for data transmission. It is also a major way of computer communication.
Asynchronous transfer
Asynchronous transfer is the way of synchronous character transmission, also known as start-stop synchronization. When sending a character code, the character is preceded by a "start" signal, the length is 1 symbol wide, the polarity is "0", that is, the space polarity; and a "stop" is added after the character is sent. The signal has a length of 1, 1.5 (used in International Code No. 2) or two symbols wide, and the polarity is "1", that is, the polarity of the mark. The receiving end can distinguish the transmitted characters by detecting the start and stop signals. Characters can be sent continuously or separately. When no characters are sent, the stop signal is sent continuously. The start time of each character can be arbitrary, the length of the symbols in one character is equal, and the receiving end detects the start of a new character by a signal to the transition of the signal ("1" "0"). The method is simple, and the clock signals of both the receiving and transmitting sides do not need to be accurately synchronized. The disadvantage is to increase the start and stop signals, and the efficiency is low, which is used in low-speed data transmission.
Synchronous transmission Synchronous transmission is a bit (symbol) synchronous transmission. This method must establish accurate bit timing signals on both the receiving and transmitting sides to correctly distinguish each data signal. In transmission, data is divided into groups (or frames), and one frame contains multiple character codes or multiple independent symbols. Before the data is transmitted, a predetermined sequence of frame synchronization symbols must be added at the beginning of each frame. After the receiver detects the sequence flag, the start of the frame is determined, and synchronization between the two parties is established. The receiving end DCE extracts the bit timing signal from the received sequence to achieve bit (symbol) synchronization. Synchronous transmission does not add up and stop signals, and the transmission efficiency is high. It is used for data transmission above 2 400 bit/s, but the technology is more complicated.
Fancy Usb Flash Drive,Pvc Usb Stick With Logo,Stock Usb Flash Drive,Usb Flash Drive Features,custom PVC USB flash drive
Shenzhen Konchang Electronic Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.konchangs.com