Circuit Switched (CS: circuit switching) is an exchange of communication networks first appeared, is the most common type of exchange, mainly used in telephone communication network, the telephone exchange is completed, more than 100 years of history.
The process of telephone communication is : first off-hook, dialing after hearing the dial tone, the switch looks for the called party, and sends a ringing tone to the calling party while ringing the called party. This indicates that the caller has been established between the calling and the calling party. The two-way voice transmission path; when the called party picks up the phone, it can enter the call phase; during the call, if any party hangs up, the switch destroys the established call path, and sends a busy tone to the other party to hang up, thereby ending the call. . As can be seen from the description of the telephone communication process, telephone communication is divided into three phases: call setup, call, and call teardown. The process of telephone communication, that is, the process of circuit switching, therefore, the basic process of corresponding circuit switching can be divided into three stages of connection establishment, information transmission and connection removal.
1. The transmission delay of information is small, for one connection. The transmission delay is fixed;
2. The information is transmitted "transparently" in the data path in the form of digital signals. The switch does not store, analyze, and process the information. Therefore, the overhead of the switch is small, and no additional control information is needed for the data information. The transmission efficiency is relatively high;
3. The coding method and information format of the information are coordinated by the communication parties and are not restricted by the network.
Circuit switching disadvantage1. Although the delay of information transmission is small, the connection time of the circuit is longer;
2. The circuit resources are monopolized by both parties, and the utilization rate of the whole circuit is low;
3. The communication parties should be fully compatible in terms of information transmission, coding format, synchronization mode or communication protocol, which limits the direct interworking of user terminals of different speeds, different code formats and different communication protocols;
4. There is call loss, that is, there may be a call failure due to the busyness of the other party's user terminal equipment or the overload of the switching network.
Circuit switched classificationCircuit switching is divided into two methods: Time Division Switching (TDS) and Space Division Switching (SDS).
Time-division exchange is to divide time into a number of non-overlapping time slots, establish different sub-channels by different time slots, complete time slot shifting of voice through time-slot switching network, and realize voice exchange between incoming and outgoing lines. Exchange method. The key to time-division exchange is the exchange of time slot locations, which is controlled by the calling dialer. In order to implement time slot exchange, a voice memory must be set. In the sampling period, n time slots are respectively stored in n memory cells, and the inputs are stored in the order of time slots. If the outputs are read out in a particular order, this can change the order of the time slots and enable time slot switching.
Space-switching refers to the entry of an incoming line in the exchange process by selecting the outgoing line in the space and establishing a connection. After the communication is over, it will be removed. For example, one end of the cord on the manual switch is connected to the plug hole, and the operator connects the other end of the cord to the called plug hole according to the caller's request. This is the most vivid air exchange mode. In addition, electromechanical (electromagnetic mechanical or relay), stepper, crossbar, semi-electronic, program-controlled analog subscriber switches and broadband switches can use the space-switching principle to achieve the exchange requirements.
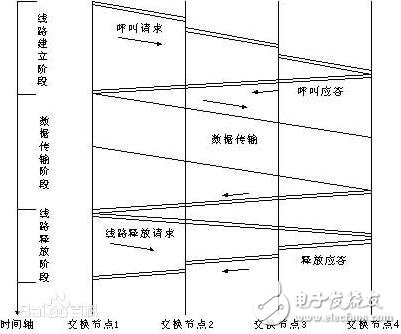
Three stages of circuit switchingThe whole process of circuit switching includes three stages: establishing a line, occupying a line, and transmitting and releasing a line. The following are introduced separately.
(1) Circuit establishment
Just as a call must first establish a path between the two parties through dialing, the circuit-switched mode of data communication must also establish an end-to-end circuit through the call process before transmitting the data. Its specific process is as follows.
1 Initiation sends a request to a terminal station (responder site), which is transmitted to the destination through the intermediate node.
2 If the intermediate node has an idle physical line available, receive the request, assign the line, and transmit the request to the next intermediate node; the entire process continues until the end. If the intermediate node has no free physical lines to use, the connection to the entire line will not be possible. The data transfer phase is allowed only after a physical line is established between the two sites of communication.
Once the 3 lines are assigned, other stations will not be available until they are released, even if there is no data transmission on the line at some point.
(2) Data transmission
After the circuit switched connection is established, data can be sent from the source node to the intermediate node, and then exchanged by the intermediate node to the terminal node. Of course, the terminal node can also send data to the source node via the intermediate node. This type of data transmission has the shortest propagation delay and no blocking problems unless there is an unexpected line or node failure that interrupts the circuit. However, it is required that the established circuit must remain connected during the entire data transmission process, and the information transmission delay of both communication parties depends only on the delay of the electromagnetic signal transmission along the media.
(3) Circuit removal
When the data transfer between the stations is completed, the action of releasing the circuit is performed. The action can be initiated by any station, and the release line request is sent to the other party through the intermediate node passing through, releasing the line resources. Once the removed channel is idle, it can be used by other communications.
Circuit switching example: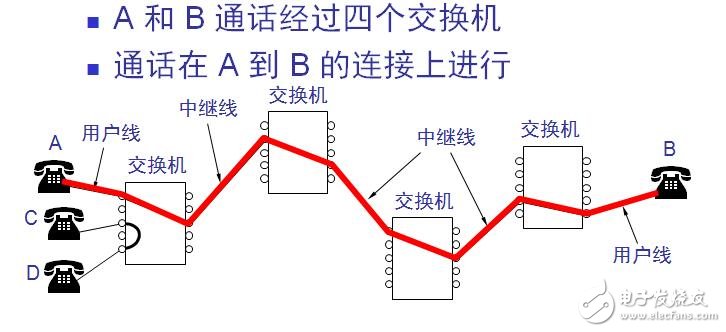
Description
-Contact Resistance:≤50mΩ
-Insulation Resistance:≥100mΩ
-Dielectric Strength:1,500V,
-1min Electronic Life:10,000 cycles
-Operating temperature:T120
-Rating current/voltage:6A 250V AC
Features
â—† Small Compact Size, high reliability
â—† Micro contact gap,high speed operation,high sensitirity,Micro operatizon travel.
â—† Long life & high reliability
Rotary Switch,Rotary Limit Switch,Car Rotary Switch,Rotary Snap Switch
Ningbo Jialin Electronics Co.,Ltd , https://www.donghai-switch.com