PROFIBUS is an international, open, field bus standard that does not rely on equipment manufacturers. Widely used in manufacturing automation, process automation and other areas of buildings, transportation, electricity and other automation. PROFIBUS consists of three compatible parts, namely PROFIBUS-DP (Decentralized Periphery), PROFIBUS-PA (Process Automation), and PROFIBUS-FMS (Fieldbus Message Specification).
(1) PROFIBUS-DP: A high-speed, low-cost communication used for communication between equipment-level control systems and decentralized I/O. Use PROFIBUS-DP to replace 24VDC or 4-20mA signal transmission. The polling communication method is adopted between the master station and the slave station, and is mainly applied to the unit level and the field level communication in the automation system.
(2) PROFIBUS-PA: Designed specifically for process automation, sensors and actuators can be connected to a single bus with intrinsic safety specifications. The power and communication data are transmitted in parallel via the bus, and are mainly used for cell-level and field-level communication in process-oriented automation systems.
(3) PROFIBUS-FMS: It is used for the workshop level monitoring network and is a token structure and real-time multi-master network. Defines the communication model between the master station and the master station. It is mainly used for the exchange of process data between the system level and the plant level in the automation system.
PROFIBUS protocol structureThe PROFIBUS protocol structure is based on the ISO 7498 international standard and uses Open System Interconnection (SIO) as a reference model. The OSI model is the basis of fieldbus technology. For industrial control of the underlying network, the amount of information controlled by a single node is small, and the task of information transmission is relatively simple, but the requirements for real-time and rapidity are relatively high. Most of the communication models used in fieldbuses are simplified to varying degrees on the basis of the OSI model.
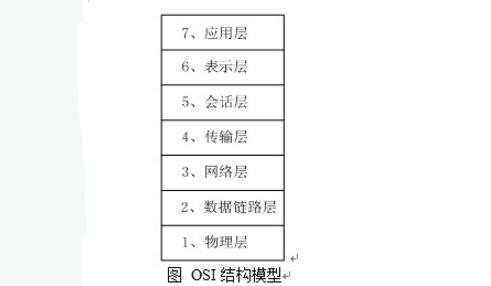
(1) PROFIBUS-DP: Layers 1, 2 and user interfaces are defined. Layers 3-7 are not described. The user interface specifies the user and system as well as application functions that can be called from different devices, and details the device behavior of various PROFIBUS-DP devices.
(2) PROFIBUS-FMS: Layers 1, 2, and 7 are defined. The application layer includes Fieldbus Message Specification (FMS) and Lower Layer Interface (LLI). FMS includes application protocols and provides users with a wide selection of powerful communication services. LLI coordinates different communication relationships and provides device-independent Layer 2 access interfaces.
(3) PROFIBUS-PA: PA's data transmission uses the extended PROFIBUS-DP protocol. In addition, the PA also describes the PA profile of field device behavior. According to the IEC1158-2 standard, PA's transmission technology ensures its intrinsic safety, and it can provide power to field devices via the bus. Use the connector to expand the PA network on the DP.
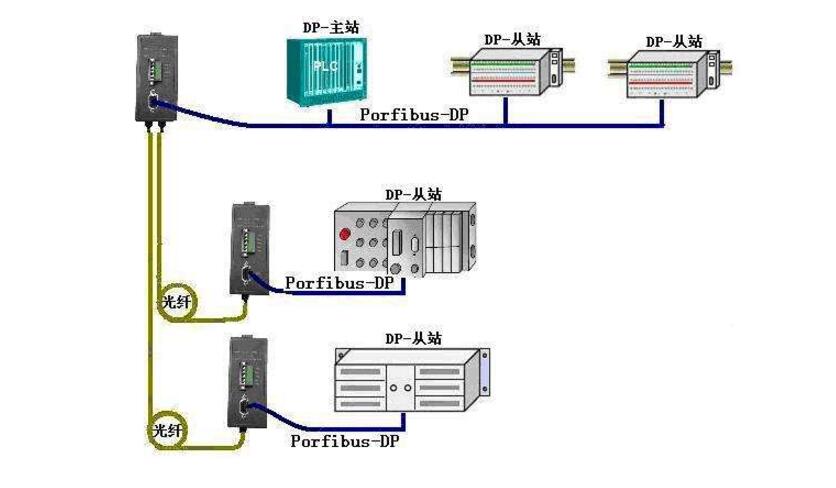
Profibus enables decentralized digital controllers to be networked from the ground floor to the plant floor. Compared with other field buses, Profibus has the important advantage of having a stable international standard EN50170 as a guarantee, and it has universality through practical application verification. It includes Processing, manufacturing, process, and digital automation are used in a wide range of applications, and can be achieved in three ways: centralized control, decentralized control, and hybrid control. The system is divided into master station and slave station:
The master station decides the data communication of the bus. When the master station obtains the bus control authority (token), it can send messages without external requests. The master station is also called an active station in the Profibus protocol.
The slave station is a peripheral device. Typical slave stations include: input/output devices, valves, actuators, and measurement transmitters. They have no bus control and only acknowledge the received message or send a message to the master when it requests it. Slave stations are also called passive stations. Since the slave only requires a small part of the bus protocol, it is particularly economical to implement.
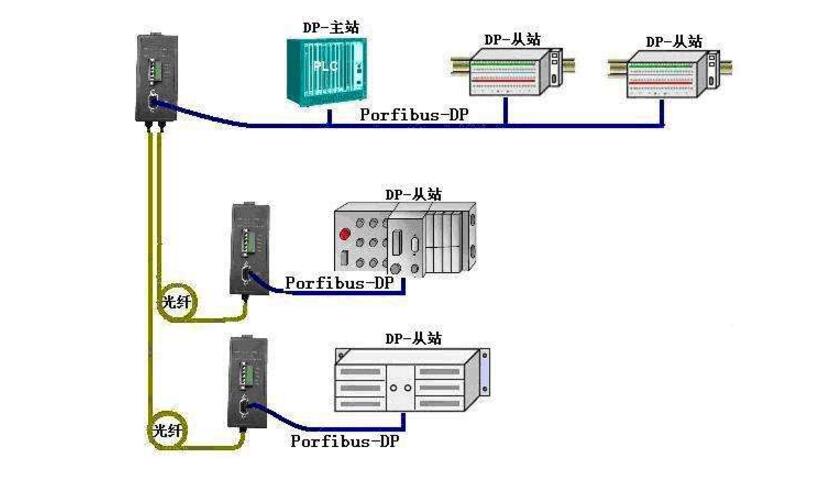
The communication media access method of PROFIBUS is a distributed token method, which is a time triggered network protocol. Between the master nodes is the token ring transmission mode, and the master node and the slave node are master-slave polling. When the master node gets the token, it allows it to communicate with the slave node and/or other master nodes for a certain period of time. The maximum time for the token to cycle through all the master nodes (set period TTR) is pre-determined and determines the length of the token's specific retention time at each master node. The data transmission between the master nodes must ensure that the master node has sufficient time to complete the communication tasks within the pre-defined time interval, and the data exchange between the master node and the slave nodes should complete the data transmission as quickly and easily as possible.
To this end, the Media Access Control MAC protocol of PROFIBUS sets up two types of clock timers: one is a token running cycle timer, which is used for the token's actual running time TRR timing; the other is a licensed timer for The master node token holding time TTH counts, and when the token reaches a master node, the node's periodic timer starts timing.
When the token reaches the master node again, the MAC assigns the difference between the TRR value of the periodic timer and the set period value TTR to the licensed timer, ie TTH=TTR-TRR, and the licenser controls the information according to the value. Transmission.
When the licensed timer control information is sent, if the token reaches the timeout, that is TTH "0", then this node can only send a high priority information; if the token arrives in time, then the node can continuously send more than one waiting to send After the high-priority information has been sent, until all the high-priority information has been sent, or the license time has passed. If all the high-priority information to be sent still has the license time, the low-priority information can be sent in the same way. Regardless of whether to send high priority or low priority information, whether or not the license time expires is detected before sending, instead of checking in advance whether the message has timed out. This detection method means that the message sending inevitably causes the license time to expire. Affects the implementation of periodic real-time communications.
This kind of power supply is also called industrial switching mode power supplies (SMPS) – It is a type of AC to DC, it obtains energy from the power grid, a DC high voltage is obtained through high voltage rectifier filtering, DC/DC Converter obtains one or more stable DC voltage at the output end, and the power can be produced from several watts to several kilowatts for different occasions. The specifications of switching power supply are various, the standard are 5V 12V 24V LED Power Supply, including single output, dual output and triple output power supply. They are widely used for LED strip, led module, led lamp and CCTV camera.
Power Supply,Switching Power Supply,Switch Mode Power Supply,12V DC Power Supply
Shenzhen Yidashun Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.ydsadapter.com