The software defined optical network (SDON) architecture realizes the tight coupling between the control function and the transfer function to the tight coupling of the control function and the operation function, and the closed control with the connection process as the core to the core of the networking process. The mode change of open control represents a new development direction of future optical network technology and application. The main advantages of SDON technology are:
â— The SDON solution can solve the interconnection problem between heterogeneous networks. With the development of converged network technologies, different types of services and network resources are intertwined, forming an isolating network interconnection environment, which exacerbates the difficulty of network-wide service control and resource management. The scheme expands the related protocols such as Openflow and develops an object-oriented interactive control interface, which can realize heterogeneous network information abstraction and cross-layer network control integration, thereby accessing the network and the core network, the data network and the optical network, A new heterogeneous network architecture system with unified control capabilities is established between the wired network and the wireless network.
â— SDON can meet the needs of users for optical network orchestration, so as to achieve flexibility in the use, operation and sales methods of network devices, and enable users to obtain desired service functions at a faster speed without waiting for equipment vendors. These features are incorporated into proprietary devices.
â— SDON can bring virtual management of optical network resources. The network equipment of virtualized management can cover all OTN products. The virtualization technology of network resources can better utilize the advantages of network infrastructure resources and open unified resources. The management platform optimizes the utilization of network resources. Based on the network architecture of virtualization, it is possible to quickly and efficiently access and control network resources under the premise of ensuring service quality according to the application needs of different services.
In recent years, although SDON technology research is still in its infancy, as a hot technology combining SDN and optical network, it has been highly valued by major operators and equipment vendors at home and abroad. From August to September 2014, the Optical Internet Forum (OIF) and the Open Network Fund (ONF) jointly organized a number of operators, equipment manufacturers and scientific research institutions around the world to carry out SDN-based optical transport network OTN prototype and interoperability testing and Demo. In this demonstration, China Telecom led and jointly cooperated with ZTE, Huawei and Bonfire to complete China's first SDON cross-vendor and multi-domain networking test at China Telecom Beijing Research Institute. This test verifies the feasibility of a multi-domain SDON technology solution based on a hierarchical controller architecture, marking a breakthrough in the commercialization of SDON. The multi-domain SDON solution of the hierarchical controller architecture is shown in Figure 1. The features of the technical solution are as follows.
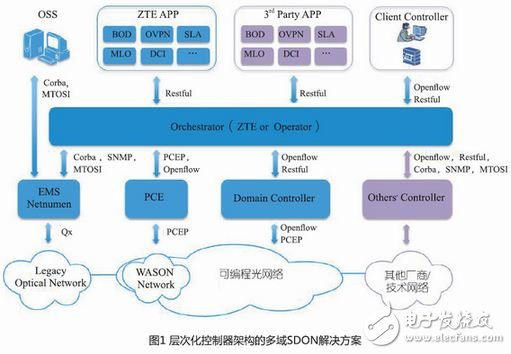
â— The entire architecture is divided into four layers from top to bottom: APP application layer, Orchestrator total controller layer, single domain controller layer and OpTIcal Network device layer.
â— The North Bound Interface (NBI) between the APP application layer and the Orchestrator master controller focuses on the Restful interface mechanism. The Restful mechanism draws on the architectural style of Web services, and has the technical advantages of stateless, resource-oriented, simple and efficient, loosely coupled, and scalable, thus providing SDON's open control, programmable, and definable technical features for the northbound interface. Natural technical support.
â— The South Bound Interface (SBI) between the single-domain controller layer and the OpTIcal Network device layer is compatible with WASON (Automated Switched Optical Network) and the earlier deployed OTN network to ensure the interconnection between the SDON network and these network devices. Interoperability, better adapt to the operator's smooth upgrade and progressive evolution of service deployment.
With the continuous deepening of SDON technology research, industry vendors and organizations have gradually discovered that the virtualization of optical networks is the basis and premise for implementing SDON-based open control, and is also a major component of SDON controllers. Broadly defined network virtualization, usually referred to as virtualization for data networks - divides traditional data network service providers into two types: infrastructure providers that manage the physical layer infrastructure; service providers, based on infrastructure The provider's resources are integrated to create a virtualized network; ultimately, end-to-end services are provided to end users on the basis of resource integration. Broadly defined network virtualization is to enable a physical network to support multiple logical networks at the same time. Virtualization preserves the original hierarchical structure, data channels and services that can be provided in the network design, so that the end user experience is the same as the exclusive physical network. At the same time, network virtualization technology can also make efficient use of network resources: space, energy, equipment capacity, etc. For example, a company or its data center can virtualize a lot of networks when it has a set of physical infrastructure, and provide services for the company's operation and maintenance department, new mergers, and important departments that need to be isolated. Each virtual network and physical network have the same. safety.
For SDON, network virtualization is an important part of supporting network structure diversification. It can be defined as follows: It supports the network architecture of multiple operators at the same time, sharing the same physical layer, which is also managed by multiple equipment vendors; It supports the use of a series of open and programmable network interfaces and creates a virtual abstraction layer for network devices at the physical layer; allows users to control the abstraction layer and change the corresponding network state, and shields the user from the physical layer network. And the complexity of use makes it easier for users to deploy new applications on the abstraction layer, which greatly increases the flexibility of network applications.
The main difference between network virtualization and generalized network virtualization in SDON is the realization of the main body of virtualization. Often, SDN is believed to separate data network functions from stand-alone, decentralized hardware platforms and manage these components in the form of virtual machines. Network virtualization in SDON will simplify and generalize network functions and network activities, such as shielding physical plane details and automating planning, configuration, management, optimization, and protection recovery. The manual operation and planning process are also evolving toward virtualization. The increased degree of automation and flexibility allows operators to reduce the load on high-level work and put it at a lower level, including the optoelectronic level. For example, in non-automated networks, people often use multiple redundant systems to protect nodes. Failure, but it is costly; automation networks restore traffic by rerouting network failures, reducing reliance on expensive, large redundant systems.
In the SDON architecture, the main purpose of virtualizing optical networks is to virtualize the physical layer infrastructure of the optical network, thereby completing the abstraction and encapsulation of optical network services, and separating the services provided from the physical layer network facilities. On, provides a programmable, definable optical network virtual layer for upper-level users. This will have a profound impact on the future development of optical networks: operators can pass control of optical network infrastructure to application layer users through interfaces open to application layer users, optical network virtual layers, etc.; Open some or all of the optical resources of the optical network virtual layer, allowing users to access and control according to their own needs on the basis of available virtual optical network resources - allowing users to integrate and define network resources themselves, thereby achieving "optical network" Resources as a service, that is, the technical concept of OaaS (OpTIcal as a Service).
Since 2014, research on optical network virtualization technology and applications has received widespread attention in the industry. Soon-known vendors including ZTE, ADVA, Huawei, and JDSU will deploy SDON to support optical network virtualization in next-generation optical networks. The system" is the focus of the development of optical network service technology. As the basic resource of data center interconnection, the virtualized application scenario is generally considered to greatly simplify the work of network operators.
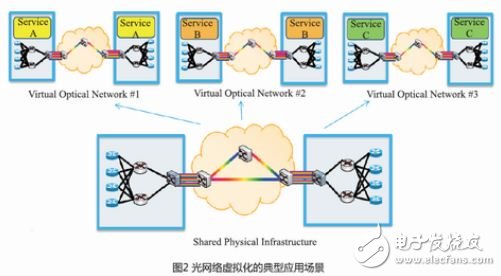
Figure 2 shows a typical application scenario for optical network virtualization: each data center service has its own specific QoS and SLA requirements. Therefore, the network operator needs a dedicated OTN network, which can share the unified physical OTN network device through the virtual optical network. On the basis of meeting the various business needs of different data centers.
So far, although optical network virtualization is a key technology of SDON, it has been widely valued by industry manufacturers and scientific research institutions. However, due to many technical difficulties, it is still in the stage of theoretical analysis and experimental research. Technical difficulties mainly include:
â— How to provide scalable, flexible, and configurable network application services, including: implementing end-to-end service connections and OVPN control across multiple management domains; how to provide dynamic connection services based on user requests, that is, BoD services; Provide end-to-end connectivity - guarantee low QoS, low latency and other QoS; have the ability to allocate bandwidth on demand, reach wavelength level or sub-wavelength level, time controllable (minutes, hours or days); how to network resources Coordination with other important network resources such as CPU, storage and visualization display devices, broadcast/multicast capabilities, etc.
â— Abstraction encapsulation of optical network resources, that is, how to abstract the mathematical model of the optical network physical layer resource model. In particular, optical network resources and transmission modes have their own physical characteristics, such as optical networks that are different from other networks. Physical layer loss: How to abstract the physical layer loss of these optical networks into the optical layer of the optical network due to the characteristics of the optical signal transmission itself, the accumulation of various physical layer optical channel impairments such as dispersion, polarization mode dispersion, and gain jitter.
â— Virtualized optical network resource mapping problem, which allocates physical resources required for runtime to virtual nodes and virtual links in virtual optical network service VONS, and designs optimized solution objective functions (such as infrastructure resources) for different mapping allocation strategies. Load balancing, maximizing network currency revenue, maximizing resource utilization efficiency, optimizing service quality, maximizing the number of end users, etc., optimizing mathematical models and optimization algorithms, etc., to meet the user's personalization and performance of optical network use. Benefits and other needs.
All of the above are issues that need to be solved in optical network virtualization technology. Research on optical network virtualization technology has a long way to go, but the benefits and value it can bring are immeasurable, and represent the way forward for the development of SDON technology.
Poly Solar Cell,Solar Photovoltaic Cell,Most Efficient Solar Cell,Polycrystalline Solar Cells
Wuxi Sunket New Energy Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.sunketsolar.com